Boat Navigation Lights Rules: Illustrated Beginners Guide
When navigating at night, the lights on other boats are your first clue about the moving dangers around you. And your navigation lights are your first line of safety in avoiding collisions in the dark, and they tell others vessels what you are and what you are doing. The rules sound complex, but with a little understanding you can get the basics for any situation.
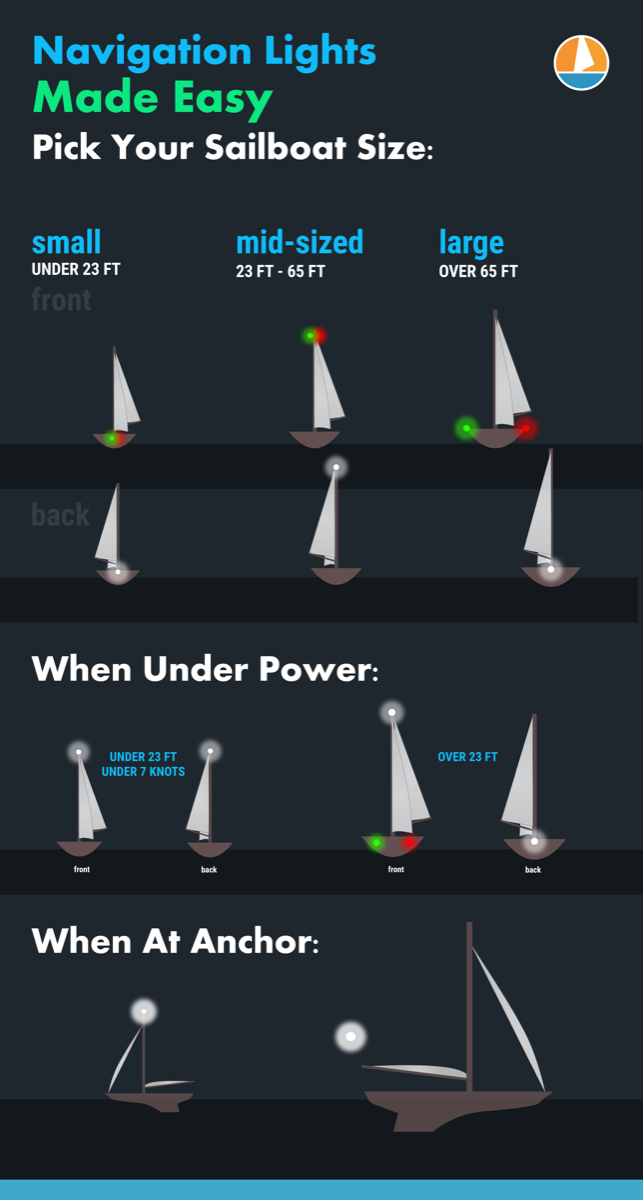
So what are the basic navigation light rules? For most small vessels, motoring requires red and green (port and starboard) lights, and a white light visible in all directions around the boat. This is almost always a stern light and a masthead light on sailboats. Boats under sail require port and starboard lights, and a white stern light. Sailboats below sixty-five feet may show a tricolor light at the masthead instead of side and stern lights when sailing.
That's it, in a nutshell. There's a little more to it, as the rules change with different sizes and there are some specifics about angles of display for the colors. Identifying other ships at sea requires more study, but the basics are the same. And it's not much trouble to make sure you've always got the proper lights on your vessel.

On this page:
What are the official colregs rules for your sailboat, what about the uscg (united states coast guard) rules, lighting at anchor, identifying the boats around you.
The International Regulations for the Prevention of Collision at Sea , abbreviated "COLREGS" is very specific about the lights required, their shapes and sizes, and the distance they must be visible. For the smaller boat, the following definitions apply.
- Masthead Light - a white light placed centerline on the boat showing an arc of 225 degrees with 112.5 degrees either side of the front of the vessel.
- Sidelights - A red light on the port side and a green light on the starboard. They must show an arc of 112.5 degrees from centerline of the bow.
- Stern light - A white light on the stern of the boat showing an unbroken arc of 135 degrees from centerline of the vessel.
- All-round light - A light showing in an unbroken arc of 360 degrees.
The good news is you need not measure these angles. Any properly installed USCG or COLREGS approved light which will cover the correct arcs. If you have to replace the original light from your boat, make sure it's with an approved replacement.
Lights When Sailing
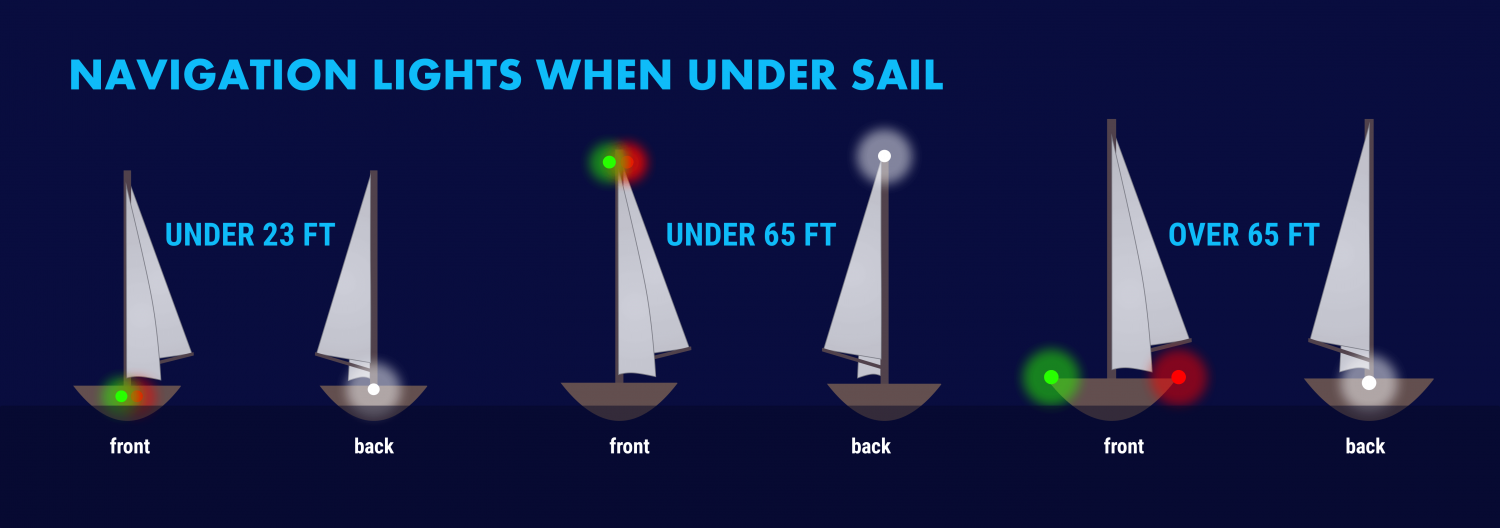
The specific rules for a sailboat under sail are in COLREGS Rule 25 and vary slightly with the size of the boat. A sailboat powering is considered a power boat and falls under in Rule 23.
- Under 23 feet (7 meters) - side lights and a stern light, possible. If these lights can not be displayed a light must be kept at hand to help avoid a collision. This can be a bright flashlight.
- Over 23 feet - Side lights visible to one nautical mile and stern light visible for two.
- Vessels under 65 feet may combine both sidelights into a single lantern on the bow.
- May show a tricolor light on the masthead instead of sidelights and a stern light. It's one or the other though, do not show these lights at the same time .
- Masthead light must be visible for three nautical miles, all other lights must have a two nautical mile visibility.
- Side lights must be separated.
- May not show a masthead tricolor light.
- Masthead light must have five nautical mile visibility, all other lights must be visible for two nautical miles.
- Optional masthead lights - any vessel under sail may display a red light over a green light at the masthead with sidelights and stern light. The red over green may NOT be displayed with a masthead tricolor light. It's one set or the other.
Lights When Motoring

For all navigational purposes a sailboat under power is considered a power boat. This includes motor sailing - if the engine is on and providing propulsion you are on a power boat, even if the sails are up . This applies to navigation lighting, sound signals in fog and limited visibility, and rights of way.
Sailboats under 50 meters under power need to show:
- A masthead light
- Stern light
A power-driven vessel under 23 feet (7 meters) that does not exceed seven knots of speed may display an all around white light, though sidelights should be used if available.

The USCG has published its own "Rules of the Road" that are based on the COLREGS. In addition, it has rules for the "Inland Waterways" for rivers, inland lakes and the Great Lakes.
The good news is this has no impact on what you have to do with your own boat.
They mostly relate to lighting changes on towed vessels like barges and tugs. For example, a vessel towing or pushing another vessel in the ocean under COLREGS shows two masthead lights, sidelights and a stern light, whereas in Inland Waterways the towing or pushing vessel displays two yellow towing lights instead of a white stern light.
If you sail on lakes, rivers or the Great Lakes where towed commercial traffic is common you should learn the inland lights, but coastal or ocean sailors will never see these.
When you anchor outside a designated mooring field, you should display an all around white light at the masthead or as high in the boat as practical.

If your boat is large and has a very tall mast, you may wish to display another light closer to the waterline. Boats approaching in the dark may not see a light on a mast sixty or seventy feet in the air when they are close to your boat.
We use a simple garden path light on our stern when we anchor, left in a rod holder or flag socket. It comes on automatically at dusk and is a cheap and easy way to be more visible. There is no specific rule stating you can not display more lights than required, or the nature of any lights beyond the required all around light.
The COLREGS also specify that a round black "daymark" should be displayed in the rigging of any vessel at anchor. Very few small vessels observe this, however it is the correct display for a vessel in an anchorage.
If you tie to a mooring in a marked mooring area you are not required to display anchor lights, but there is no harm in doing so.
The other important reason to know your lights is to figure out what's going on around you at night. The water may be ablaze with white, red, green and other lights at night and they are your first key to avoiding collisions and problems.
All combinations of lights for fishing boats, commercial vessels, and so on are outside this post‘s scope. The odds are small you will encounter a submarine, seaplane or hovercraft at night, but there are regulations regarding specific lighting for each of those vessels!
There are a few fundamentals to help you figure out what that is you see on the horizon, which way it is going, and whether it is a danger to you.
Port Wine is Red
The fundamental rule is that red sidelights will ALWAYS be on the port side of a vessel, and green lights will always be on starboard. However, some vessels can use all around red and green lights for other purposes, though those will be higher than sidelights.
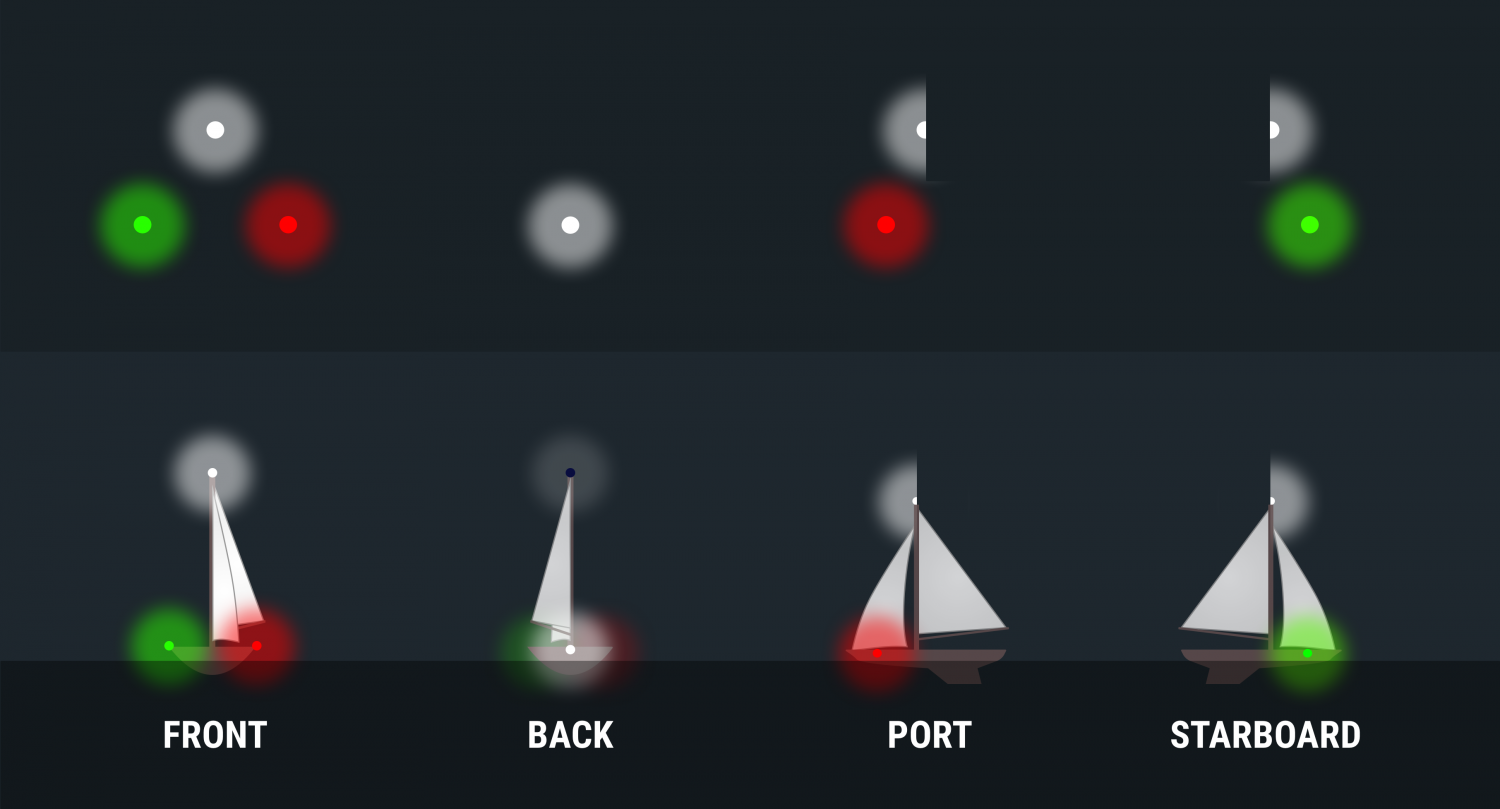
The light‘s on a ship is not important, some large tankers and freighters will have their sidelights far aft and put them on the superstructure for better visibility. It is not safe to assume that sidelights you can see are on the bow of large vessels .
When you can see the color, you know which way the bow is pointing. If it's red, it's pointing more or less to the left and will travel in that direction. A green light shows it is heading more or less to your right.
If you can see the red and green lights at the same time, you are looking directly at the bow of the vessel. When you are far away, this isn‘t as alarming as if you are close crossing. Seeing red and green lights together on a vessel is something you never want to see for long.
Be aware of red and green lights used in combination with other red, green and white lights. These may not be running lights and could have other significance.
Tankers, Freighters and Large Ships
Tankers, freighters and large ships will have side lights, a stern light and a masthead light. In addition, on vessels over 50 meters there will be a second masthead light further aft and higher than the forward light. The masthead light positions are a better tipoff to the bow direction and how far from the bow the sidelights might be. Remember - on a large vessel the sidelights may not be at the bow or even close to it.
USCG Inland Rules allow for a second all-around white light on large vessels on the Great Lakes instead of a second masthead light.
Fishing Boats
Fishing boats engaged in fishing will have more complex light displays. When they aren't fishing, they will show lights like any power vessel, but Rule 26 spells out light combinations that vary by the fishing activity being done. In general:
- Boats which are Trawling but not making headway will display a green all-around light over a white all-around light , and a masthead light aft of these lights. Boats making headway while trawling will show these lights, plus sidelights and a stern light.
- A vessel fishing other than trawling will show a red all-around light over a white all-around light . When making way they will also show sidelights and a stern light.
- If a vessel has gear more than 150 meters away from the boat, it will show a second all around light in the direction of the gear. The best rule is to give fishing boats as wide a berth as you can at night. They're easy to pick out if you check the top light configurations but their course may be difficult to predict.
Towing and Pushing
Towed vessels can be the most dangerous to cross, but they have the most lights to tell you what is happening. Refer to COLREGS or the USCG Rules of the Road Rule 24 for all combinations You can pick a tow/push vessel out with the following lights:
- Two or three masthead lights in a vertical line. Three masthead lights shows a tow over 200 meters. Additional masthead lights may show for larger tow vessels.
- A towing light (yellow light with the same characteristics as a stern light) directly above the stern light.
- The will also have side lights and a stern light.
- The towed vessel will show sidelights and a stern light. Lighting may vary under USCG inland rules, where towing lights may replace stern lights. Learn these differences if this is your regular cruising ground. If you think there is a tow ahead of you, always go well behind the aft most set of lights. Never go between a tow and avoid crossing ahead if possible as it may restrict their maneuverability.
Special Situations
There are several rare situations you may encounter. As a general rule, if there are a lot of lights and you don't understand them look for the sidelights on a moving vessel. If you can find them and figure out the direction it is moving, it makes the vessel easier to avoid. Stay well clear of lights you do not understand if you can avoid them without risk.
Most of these signals are used by larger, commercial vessels and you will not need them.
They use these light combinations with other light combinations. For example a towing vessel may also be restricted in maneuverability, and a vessel constrained by draft will show running lights if moving.
- Not Under Command - two all around red lights in a single line
- Restricted in Ability to Maneuver - red, white then red in a single line
- Constrained by draft - three all around red lights
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

What is a Properly Lit Sailboat at Night? (A Guide to Safety Regulations)

Have you ever been out on the open water and seen a sailboat with its lights on at night? It’s a beautiful sight to behold.
But did you know that there are specific safety regulations in place for properly lit sailboats? In this guide, we’ll be looking at the importance of having a properly lit sailboat, what types of lights are needed, how to install them, and how to test for proper operation.
Let’s get started and learn how to stay safe on the waters!
Table of Contents
Short Answer
A properly lit sailboat at night is a boat that is equipped with the correct navigation lights, which are required by law.
These lights must be visible for two miles and should include a green light on the starboard side, a red light on the port side, and a white light aft.
Additionally, the boat must also have a white masthead light that is visible for three miles.
The masthead light should be mounted at least two meters above the hull.
What Are the Safety Regulations for Properly Lit Sailboats?
When it comes to sailing at night, safety is of the utmost importance.
Properly lit sailboats ensure that they are visible to other boats, which reduces the risk of collisions and other accidents.
In order to ensure that a sailboat is properly lit at night , there are certain safety regulations that must be followed.
First and foremost, the sailboat must have the correct lighting equipment installed and in good working order.
This includes running lights (red and green lights found at the bow and stern of the vessel), an anchor light (a white light mounted on the masthead or the bow of the vessel), a stern light (a white light placed at the stern of the vessel), and a masthead light (a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel).
The running lights, anchor light, and stern light must be visible for at least 3 miles in clear conditions.
This allows other boats on the water to easily spot the sailboat, even in the dark.
The masthead light must be visible for at least 2 miles in clear conditions.
This ensures that the sailboat is easily seen from all directions.
In addition to having the correct lighting equipment, sailboats must also be equipped with a white all-round light.
This light must be visible for at least 2 miles in clear conditions and must be mounted on the mast at least 9 meters (or 30 feet) above the waterline.
The all-round light is an important part of a sailboats lighting system as it allows other boats to easily spot the sailboat from any direction.
These are just a few of the safety regulations that must be followed when it comes to properly lit sailboats.
Following these regulations will help to ensure that a sailboat is visible to other vessels on the water and will help to reduce the risk of accidents and collisions.
It is important that all sailors understand and adhere to these regulations in order to remain safe on the water.
Types of Lights Needed for Proper Lighting

When it comes to lighting a sailboat at night, there are a few key components that must be in place in order to ensure the safety of the vessel and the crew.
The most important of these components is the correct type of lighting equipment.
This includes various running lights, anchor lights, masthead lights, and stern lights.
Running lights are the red and green lights that are mounted on the bow and stern of the vessel, and are used to show the direction of travel of the boat.
They must be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions, making it easier to spot the boat in the dark.
Anchor lights are white lights that are mounted on the masthead or the bow of the vessel, and are used to show that the boat is anchored.
They must also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
The stern light is a white light placed at the stern of the vessel.
This is used to show the direction of travel of the boat and should also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
Finally, the masthead light is a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel.
This light is used to help identify the boat to other vessels on the water, and must also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
Having all of these lights in good working order is essential for the safety of the boat and the crew.
It is important to make sure that all lights are visible from a distance of 3 miles in clear conditions, as this will make it easier to identify the boat in the dark.
It is also important to make sure that all lights are regularly inspected and maintained in order to ensure that they are in good working order.
How to Install the Lights
Installing the lights for a properly lit sailboat at night is an essential part of staying safe while sailing.
It is important to ensure that all of the lights are in good working order and that they meet the safety regulations for visibility.
The first step is to select the right lights for your vessel.
There are two main types of lights running lights and anchor lights.
Running lights are the green and red lights found at the bow and stern of the vessel, while anchor lights are white lights mounted on the masthead or bow of the vessel.
Once the lights are selected, the next step is to install them.
Start by attaching the anchor light to the masthead or bow of the vessel.
The anchor light should be securely mounted and wired in accordance with the manufacturers instructions.
Next, attach the stern light at the stern of the vessel.
This should also be securely mounted and wired in accordance with the manufacturers instructions.
Finally, attach the running lights.
These should be mounted at the bow and stern of the vessel.
It is important to test the lights after installation to make sure they are working properly.
Make sure that the lights meet the visibility requirements of 3 miles in clear conditions, as this is the minimum distance that the lights must be visible from.
Once the lights are installed and tested, youre ready to set sail in the dark!
Importance of Properly Lit Sailboats

When it comes to sailing, safety is of the utmost importance.
This is why it is essential for all sailboats to be properly lit at night.
Having the correct lighting equipment installed and in good working order is a critical component to ensure visibility and the safety of everyone on the water.
Not only does having properly lit sailboats maintain the safety of the sailors on the boat, but it also helps to prevent collisions with other vessels.
It is much easier to spot a sailboat on the water at night when it has the correct lighting equipment, such as running lights, anchor lights, stern lights and masthead lights.
All of these lights should be visible for at least 3 miles in clear conditions, making it much easier to spot a sailboat on the water.
Additionally, having properly lit sailboats at night is also important for law enforcement and marine patrol officers.
It makes it easier for them to identify and inspect boats, ensuring that all safety regulations are being followed.
This helps to keep the waterways safe for all boaters.
For these reasons, it is important for all sailboats to be properly lit at night.
By having the right lighting equipment installed and in good working order, it can help to maintain the safety of everyone on the water, as well as help to prevent collisions with other vessels.
It also makes it easier for law enforcement and marine patrol officers to identify and inspect boats, helping to keep the waterways safe for all boaters.
Different Types of Lights and Their Functions
When it comes to lighting a sailboat at night, there are several different types of lights that must be installed and in good working order in order to ensure the safety of the vessel and its occupants.
The most common types of lights used on sailboats are running lights, anchor lights, stern lights, and masthead lights.
Running lights are the green and red lights found at the bow and stern of the vessel.
These lights are typically used to signal the direction of the boats movement, and must be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
The green light is typically placed on the port side (left side) of the boat, and the red light is placed on the starboard side (right side).
Anchor lights are white lights mounted on the masthead or bow of the vessel.
They are used to indicate that the boat is at anchor, and must also be visible for 3 miles in clear conditions.
Stern lights are white lights placed at the stern of the vessel.
These lights indicate the boats direction of travel, and must be visible for 2 miles in clear conditions.
The masthead light is a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel.
This light is typically used in conjunction with the stern light to indicate the direction of travel, and must be visible for 2 miles in clear conditions.
In addition to these lights, boats may also be fitted with a variety of other lights such as tricolor lights, sidelights, all-round lights, and deck lights.
These lights are typically used to indicate the presence of the vessel in low-visibility conditions, and must be visible for 2 miles in clear conditions.
It is important to ensure that all lights on a sailboat are in good working order and visible from a distance in order to make the vessel visible to other boats and comply with safety regulations.
A properly lit sailboat at night is one that has the correct lighting equipment installed and in good working order.
Benefits of Properly Lit Sailboats

Having a properly lit sailboat at night is essential for staying safe on the water.
With the right lighting equipment installed and in good working order, you can be easily seen by other vessels and prevent possible collisions.
Additionally, having the right lights on your sailboat can help other boaters determine your vessels size, direction, speed, and even your intentions on the water.
Having the right lights can also give you a sense of security while youre out at night.
Knowing that youre visible to other vessels reassures you that youll be able to be seen and spotted if you need assistance or if theres an emergency.
When youre out on the water at night, having a properly lit sailboat can also make navigation easier.
By having the correct lighting equipment installed, youll be able to easily spot buoys, markers, and other vessels, making it easier for you to stay on course and reach your destination in a timely manner.
Having the proper lights also helps to keep your sailboat in compliance with safety regulations.
If youre stopped by the coast guard or other law enforcement, having the right lights can help to avoid any potential fines or penalties.
Overall, having a properly lit sailboat at night is essential for staying safe on the water.
Not only does it make it easier for other vessels to spot you, but it can also help with navigation and make sure that youre in compliance with safety regulations.
Properly lit sailboats can also give you a sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that youre visible to other vessels in the area.
How to Test Lights for Proper Operation
Testing lights on a sailboat at night is an important part of ensuring that the craft is properly lit and visible to other vessels.
It is essential for safety, as well as compliance with regulations set by the United States Coast Guard.
Before each voyage, it is important to inspect all of the lights and make sure that they are in proper working order.
The first step to testing lights is to turn them on and check that they are functioning correctly.
It is important to make sure that all of the required lights are present and that they are bright enough to be seen in clear conditions for up to 3 miles away.
The running lights should be a green light at the bow and a red light at the stern, while the anchor light should be a white light mounted on the masthead or the bow of the vessel.
The stern light should be a white light placed at the stern, and the masthead light should be a white light placed at the highest point on the vessel.
Another important step in testing lights is to make sure that they are not obstructed in any way.
This includes checking for any wires, cables, or other objects that could block the lights from being visible.
This is especially important for the masthead light, as it needs to be accessible in order to be seen from a distance.
It is also important to check the wiring of the lights to make sure that they are securely connected and not corroded or damaged.
Finally, it is important to check the bulbs of the lights to make sure that they are all functioning correctly.
It is important to check the wattage of the bulbs to make sure that they are bright enough to meet the standards set by the United States Coast Guard.
It is also important to make sure that the bulbs are not cracked or damaged in any way, as this could affect their visibility.
Following the steps outlined above will help to ensure that all of the lights are in proper working order and can be seen from a distance in clear conditions.
This is important for safety, as well as compliance with regulations set by the United States Coast Guard.
Final Thoughts
Having the correct lights installed and in proper working order on your sailboat is essential for safety and visibility on the water at night.
Knowing what type of lights you need, how to install them, and how to test them for proper operation is key.
While it may seem daunting to install and maintain all these lights, the benefits of having a properly lit sailboat at night far outweigh the effort.
So take the time to review safety regulations, and make sure you have the right lights installed and operating correctly to ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
James Frami
At the age of 15, he and four other friends from his neighborhood constructed their first boat. He has been sailing for almost 30 years and has a wealth of knowledge that he wants to share with others.
Recent Posts
When Was Banana Boat Song Released? (HISTORICAL INSIGHTS)
The "Banana Boat Song" was released in 1956 by Harry Belafonte. This calypso-style song, also known as "Day-O," became a huge hit and remains popular to this day for its catchy tune and upbeat...
How to Make Banana Boat Smoothie King? (DELICIOUS RECIPE REVEALED)
To make a Banana Boat Smoothie King smoothie at home, start by gathering the ingredients: a ripe banana, peanut butter, chocolate protein powder, almond milk, and ice. Blend the banana, a scoop of...
Sailboat Navigation Lights: A Guide to Safe Nighttime Sailing
by Emma Sullivan | Jul 26, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance

==Short answer sailboat navigation lights:== Sailboat navigation lights are essential safety features that help vessels communicate and avoid collisions at night. These lights, such as the red and green sidelights and white stern light, allow sailors to determine the direction and status of approaching boats.
Understanding the Importance of Sailboat Navigation Lights
Sailing, with its air of romance and adventure, is a timeless pursuit that has captured the hearts of seafarers for centuries. While sailing enthusiasts revel in the sense of freedom and connection with nature that this activity provides, it is crucial to recognize that safety should always be a top priority when out on the open water. Among the many precautions taken to ensure safe navigation, sailboat navigation lights play an essential role.
These lights serve as beacons in the darkness, guiding both sailors and other vessels on their watery voyages. They are particularly vital during low visibility conditions such as fog, twilight, or nightfall when discerning a sailboat’s presence can be challenging. By understanding the importance of sailboat navigation lights, sailors can take proactive steps towards avoiding collisions and mishaps while enjoying their time at sea.
First and foremost, these lights serve as a communication tool between vessels. Just as traffic signals guide drivers on roads, sailboat navigation lights communicate a vessel’s navigational status to others nearby. These lights convey critical information about a boat’s direction of travel and whether it is under power or relying solely on wind propulsion. This enables other boats to predict potential collision courses and adjust their own paths accordingly.
In terms of regulatory compliance, having properly functioning navigation lights is not just recommended; it is required by international maritime laws like The International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGS). These regulations provide clear guidelines for different types of watercraft around the world to standardize safety measures. Following these rules ensures that every sailor speaks the same language when at sea, diminishing misunderstandings and encouraging mutual respect among mariners.
Furthermore, sailboat navigation lights contribute significantly to situational awareness – an invaluable asset in any seafaring endeavor. By displaying specific colors and configurations such as red/green sidelights and a white stern light visible from 135 degrees, sailors can discern the orientation of approaching vessels even in complete darkness. This knowledge empowers sailors to make informed decisions about altering their course or speed to avoid potential dangers.
In addition to enhancing navigation safety, sailboat navigation lights also add a touch of elegance and charm to nighttime voyages. Picture yourself sailing under a summer moonlit sky, with the soft glow of your vessel’s navigation lights casting mesmerizing reflections on the water’s surface. These lights not only provide reassurance but also create an enchanting ambiance for both sailors and onlookers.
While it may be tempting to dismiss the importance of sailboat navigation lights as just another cumbersome boat regulation, understanding their indispensable role is crucial for every sailor’s peace of mind and for ensuring uninterrupted enjoyment of our beloved pastime. So next time you set sail, remember that these little beacons serve as more than mere accessories – they are your allies in darkness, silently guiding you towards safe passages and unforgettable adventures on the open sea.
How to Properly Install and Operate Sailboat Navigation Lights
When it comes to sailing, safety should always be a top priority. And one of the essential safety measures on a sailboat is proper navigation lighting. Sailboat navigation lights help other vessels identify your boat’s position and course, especially during low visibility conditions or at night. In this blog post, we will guide you through the correct installation and operation of sailboat navigation lights to make your sailing adventures safe and enjoyable.
Installing sailboat navigation lights may seem like a simple task, but there are several key factors to consider for optimal functionality. First and foremost, familiarize yourself with international regulations regarding navigation lights. These regulations ensure consistency across different countries and improve communication between vessels on the water.
Before starting the installation process, carefully choose high-quality LED lights specifically designed for sailboats. LEDs offer numerous advantages over traditional incandescent bulbs, including energy efficiency, higher light output, longer lifespan, and reduced heat emission. Additionally, LEDs are more durable and resistant to vibrations commonly experienced while sailing.
To begin installing your sailboat navigation lights:
1. Determine the appropriate locations: Positioning your navigation lights correctly is crucial to maximize their visibility and effectiveness. Refer to your boat’s owner’s manual or consult with a marine electrician to identify the ideal mounting points for each light.
2. Prepare wiring routes: Plan out the wiring routes before drilling any holes or mounting fixtures. Concealing wires within the boat’s structure not only enhances aesthetics but also minimizes potential damage caused by exposure to external elements.
3. Drill strategically: Using an appropriately sized drill bit, carefully create mounting holes following the instructions provided by the manufacturer of your chosen navigation lights.
4. Connect electrical components: Install a waterproof junction box near each light fixture to protect wires from moisture and corrosion. Make connections following color-coded standards (red wire – positive; black wire – negative), ensuring proper polarity is maintained throughout the circuit.
5. Securely attach fixtures: Once all wiring connections are made, attach the navigation light fixtures to their designated mounting positions. Double-check that they are secure and properly aligned to maintain optimal visibility.
With your sailboat navigation lights installed, it’s time to understand their operation. Different situations call for specific combinations of lighting:
1. Underway with power: When sailing under engine power, display both a red (port side) and a green (starboard side) light visible from dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft each beam. A white stern light should also be shown.
2. Sailing without power: When solely relying on wind propulsion, display just the red and green sidelights in the same manner as during powered navigation.
3. At anchor: If you’re moored or anchored, only exhibit an all-around white light at a location high enough to illuminate unobstructed from every angle.
4. Restricted maneuverability: In situations where your sailboat’s maneuverability is impaired (e.g., towing another vessel), use three shapes—two balls vertically aligned above one diamond—to indicate restricted movement.
Lastly, always ensure proper maintenance of your sailboat navigation lights:
1. Regularly inspect for damage: Routinely check for signs of wear and tear on the electrical connections, housing seals, lenses, and reflectors. Replace any damaged components promptly.
2. Clean for maximum visibility: Keep lenses clean from dirt, grime, salt residue, or any other obstructions that could limit the effectiveness of your navigation lights.
3. Carry spare bulbs/batteries: Be prepared by carrying backup LED bulbs or batteries in case of failure during extended voyages.
By following these installation steps, understanding proper operation techniques according to maritime regulations, and maintaining your navigation lights diligently; you can cruise confidently knowing your sailboat is equipped with highly visible and functional navigation lighting system—an important feature enhancing safety while enjoying the open water at any time of day or night. So, set sail with peace of mind and navigate the seas safely while embracing the thrilling adventures that await you!
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up Sailboat Navigation Lights for Safe Sailing
Welcome aboard, fellow sailors! Today, we are going to dive into the nitty-gritty of setting up sailboat navigation lights for safe sailing. As you know, proper navigation lights are an essential part of ensuring your safety on the water, especially during low-light conditions and at night. So grab your cup of coffee, sit back, and prepare to learn how to illuminate the seas like a professional.
Step 1: Know Your Lights Before we jump into the technicalities, let’s familiarize ourselves with the different navigation lights required on a sailboat. These include the red port light on the left side, green starboard light on the right side, white stern light at the rear, and if our boat is longer than 20 meters (or 65 feet), a white masthead light at its highest point. Having this knowledge sets you up for success in navigating effectively while abiding by maritime regulations.
Step 2: Choose Your Lighting System Now that we’ve covered the basics, it’s time to decide which lighting system is most appropriate for your sailboat. You have two options: traditional incandescent bulbs or modern LED lights. While both serve their purpose well, LED lights are more energy-efficient and tend to last longer – a win-win situation!
Step 3: Gathering Materials To ensure smooth sailing throughout this process (pun intended), gather all necessary materials beforehand. This includes navigation lights (either incandescent bulbs or LED lights depending on your preference), wiring connectors, heat shrink tubing (to protect connections from moisture), electrical tape, wires (preferably color-coded for easy identification), wire strippers/cutters, and mounting hardware suitable for your boat.
Step 4: Planning Placement Consideration of placement plays a crucial role in setting up navigation lights effectively. Ensure visibility from all angles without obstructing other boat equipment or compromising aesthetics onboard. Take note of any manufacturer guidelines provided with your purchased lights for optimal placement. Remember, safety doesn’t mean sacrificing style!
Step 5: Wiring Your Lights Now we’re getting hands-on! Let’s start with the stern light. Attach the wires of your chosen light to the existing electrical system using appropriate connectors and ensure a secure connection. Utilize heat shrink tubing and electrical tape to safeguard against any moisture-induced malfunctions. Repeat this process for both port and starboard lights.
Step 6: Don’t Forget the Masthead Light If your sailboat exceeds 20 meters in length, you’ll need a masthead light too. Carefully mount this light on top of your mast using suitable hardware. Then, run additional wires through the mast to connect it securely with your electrical system.
Step 7: The Proof is in Testing After successfully wiring all navigation lights, it’s time for a crucial step – testing! Double-check that all connections are secure and operational before venturing out onto the open water. Be meticulous; don’t let a faulty bulb ruin your sunset cruise or impede your journey under a moonlit sky.
Congrats, sailors! You’ve now mastered the art of setting up sailboat navigation lights for safe sailing. Remember, maintaining these lights should be an essential part of regular boat maintenance as well. With proper illumination, maritime rules adhered to diligently, and cautious seamanship skills mastered, you can enjoy many breathtaking nights on tranquil waters without compromising safety. So go forth into the starry night with confidence and raise anchor towards new horizons! Bon voyage!
Frequently Asked Questions About Sailboat Navigation Lights, Answered!
Title: Frequently Asked Questions About Sailboat Navigation Lights, Answered!
Introduction: Navigating a sailboat safely and responsibly requires understanding and adhering to various rules and regulations. One vital aspect of sailing is ensuring proper use of navigation lights. These lights not only aid in visibility but also help communicate with other vessels on the water. In this blog post, we will delve into frequently asked questions about sailboat navigation lights, offering detailed professional answers infused with wit and clever insights.
1. Why are navigation lights necessary for sailboats? Navigation lights serve as visual signals that enable sailors to identify vessel types, positions, and movements at night or in low visibility conditions. They are crucial for promoting safety on the water by helping prevent collisions and aiding in the communication between boats.
2. What are the different types of navigation lights found on a sailboat? Sailboats typically feature three main navigation lights: red (portside), green (starboard side), and white (stern light). The red light tells other sailors that your boat’s portside is facing them, while the green light indicates that your starboard side is visible. The white stern light illuminates the rear of your vessel, making it easier for others to determine your direction of travel.
3. When should I turn on my sailboat’s navigation lights? According to international rules of collision avoidance at sea, all vessels must show proper navigation lighting between sunset and sunrise or during periods of restricted visibility such as fog or heavy rain showers. It’s essential to remember that even during daylight hours if visibility drops due to poor weather conditions, switching on navigational lights can greatly enhance safety.
4. Are there any additional requirements regarding sailboat navigation lighting? Yes! Aside from displaying the three main distinct navigation lights mentioned above, it is crucial for sailboats under power or motorsailing – using engine power alongside sails – to display an additional white forward-facing masthead light apart from the stern light. This masthead light helps identify the sailboat as a power-driven vessel, providing further clarity to nearby boaters.
5. Can I use LED lights for navigation purposes on my sailboat? Absolutely! In fact, LED lights are highly recommended for their energy efficiency and prolonged lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. However, it is essential to ensure that any LED navigation lights you use adhere to relevant maritime regulations concerning color, visibility range, and intensity.
6. How can I check if my sailboat’s navigation lights are working correctly? Regular maintenance and testing of your navigation lights are vital to guarantee their functionality when needed the most. Before every outing, visually inspect each light for signs of damage or corrosion. Additionally, switch on all navigational lights while docked or at anchor to verify they illuminate brightly according to the appropriate standards laid out in navigational lighting regulations.
Conclusion: Understanding sailboat navigation lighting not only ensures your safety but also promotes effective communication with other vessels on the water. By knowing when and how to properly utilize these lights, you contribute to maintaining a harmonious sailing environment. Remember, navigating with wit means being informed and cleverly enhancing your skills as a sailor while keeping safety at the forefront of your adventures!
Top Tips and Best Practices for Maintaining Sailboat Navigation Lights
Maintaining Sailboat Navigation Lights: Expert Tips and Best Practices
Picture this – you’re out on the open water, gliding along with the wind in your sails. As the sun dips below the horizon, darkness begins to envelop your sailboat. This is when maintaining proper navigation lights becomes paramount for both safety and legal compliance. In this blog post, we will dive deep into top tips and best practices for ensuring that your sailboat’s navigation lights are not only functioning but also showcasing their brilliance.
1. Regular Inspections are Key: To ensure your sailboat navigation lights are in prime condition, regular inspections should be conducted. Make it a habit before every trip to thoroughly examine all lights, from bow to stern. Look out for any loose connections, cracked lenses, or water intrusion that could hamper their effectiveness.
2. Ensure Proper Power Supply: One common issue faced by sailors is inadequate power supply to navigation lights, leading to dimness or complete failure at crucial times. Check that the wiring system is correctly connected and working optimally. Additionally, consider installing a voltage monitor or battery analyzer to keep tabs on power levels during extended journeys.
3. Choose LED Lights: When it comes to choosing sailboat navigation lights, opt for LED technology without hesitation. LEDs offer brilliant luminosity while consuming minimal power compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Their longevity and durability make them ideal for equipping your vessel’s masthead light, sidelights, stern light, and anchor light.
4. Cleaning is Essential: Navigation lights on a sailboat accumulate dirt and grime over time due to exposure to various elements like saltwater spray or bird droppings (we all know how seagulls love making our boats their restroom). Regularly clean the lenses with a soft cloth and mild soap solution followed by drying with a lint-free towel. Keeping them crystal clear will maximize their output and visibility range.
5. Protect Against Moisture: Water ingress can be a persistent menace, harming the functionality of your sailboat’s navigation lights. To combat this, ensure watertight seals around light fixtures and wiring connections. Applying silicone lubricant or dielectric grease to connectors further enhances protection against moisture.
6. Carry Spare Bulbs and Fuses: Murphy’s Law states that anything that can go wrong, will go wrong – especially in the middle of nowhere. Imagine how disheartening it would be if one of your navigation lights suddenly fizzles out on a moonless night! Always carry spare bulbs and fuses suited for your specific lighting system to avoid such predicaments and keep your journey uninterrupted.
7. Stay Familiar with Navigation Regulations: Being updated on marine regulations regarding navigation lights is not only essential for your safety but also ensures compliance with local laws. These regulations dictate the placement, colors, and timings for displaying navigational lights based on different conditions such as underway, anchored, or sailing near other vessels at night.
In conclusion, maintaining sailboat navigation lights might seem like a mundane task; however, its significance cannot be undermined when it comes to safety during nighttime voyages. Regular inspections, adequate power supply, LED technology adoption, cleanliness, moisture protection, carrying spare bulbs/fuses, and adhering to maritime regulations should become second nature for any seasoned sailor. By following these top tips and best practices meticulously, you’ll be able to navigate the vast expanse of dark waters with confidence while ensuring a safe voyage each time.
Exploring Different Types and Designs of Sailboat Navigation Lights
When it comes to sailing at night, having the right navigation lights on your sailboat is absolutely crucial. Not only do they help you stay safe and avoid collisions with other vessels, but they also ensure that you are compliant with maritime regulations. In this blog post, we will be exploring different types and designs of sailboat navigation lights, so you can make an informed decision for your own vessel.
One of the most common types of sailboat navigation lights is the sidelight. These lights are usually mounted on either side of the boat and emit a green light on the starboard (right) side and a red light on the port (left) side. The purpose of these lights is to signal the direction in which your boat is moving to other vessels in the vicinity. Additionally, sidelights should be visible at a distance of at least two nautical miles, ensuring that other boats have ample time to react accordingly.
Another important type of navigation light for sailboats is the sternlight. As its name suggests, this light is mounted at the back or stern of the boat and emits a white light. The sternlight helps other vessels determine if you are moving away from them or approaching them from behind. It should be visible from a distance of at least two nautical miles as well.
In addition to sidelights and sternlights, sailboats also require an all-round white light, commonly known as an anchor light. This light serves as both an anchoring indicator and a warning signal to other boats that your vessel isn’t under power and may be stationary. Typically mounted atop the mast or another elevated point on the sailboat, this white light must be visible from all directions within two nautical miles.
Now that we’ve covered the main types of sailboat navigation lights, let’s delve into their designs. While traditional incandescent bulbs were once widely used for their simplicity and affordability, LED technology has revolutionized marine lighting. LED navigation lights are highly energy-efficient and have a considerably longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs. Additionally, LEDs emit a bright and focused light, making your sailboat more visible to others even in adverse weather conditions.
Furthermore, many LED navigation lights come with built-in features that enhance safety and convenience. Some models have automatic sensors that adjust the brightness of the lights depending on the ambient lighting conditions. This means that if you’re sailing during twilight or dawn, when visibility is reduced, these lights will automatically become brighter for better detection by other vessels.
Moreover, some innovative designs include combination lights that incorporate both sidelights and sternlights in one compact unit. These multifunctional lights save space on your boat while still ensuring compliance with regulations. Additionally, there are folding or telescopic navigation lights available that can be easily stowed away when not in use, further optimizing your deck space.
In conclusion, choosing the right types and designs of sailboat navigation lights is crucial for safe night sailing and regulatory compliance. Sidelights, sternlights, and anchor lights are essential components of any sailboat’s lighting system. Consider opting for energy-efficient LED technology that offers enhanced visibility and longevity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Moreover, explore innovative designs such as combination lights or folding options to optimize space onboard your vessel. By equipping your sailboat with the right navigation lights, you can navigate confidently through the darkness while captivating other sailors with your illuminated elegance on the open sea!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques

Boat Navigation Light Rules Explained (For Beginners)
Boat navigation light rules can be a little difficult for newcomers to understand. This is probably because these light rules can change depending on a wide variety of factors.
Failing to comply with these rules can leave you open to enforcement violations as well as lawsuits.
Also, knowing these rules will help keep you and other boaters safe while out on the water, so you must learn and remember them.
Here’s everything you should know about the boat navigation light rules.
Table of Contents

Why Have Boat Navigation Light Rules At All
Boat navigation light rules help boaters communicate with each other. They also help to determine who has the right of way. This is important as it determines what actions boats will take as they pass one another.
Without these guidelines, there would be many more accidents out on the water as people wouldn’t know how to interact.
Remember, when you’re out on the open water, there aren’t any designated lanes to follow, and without rules, boaters can easily become confused about which way they should turn or whether or not they should even turn at all.
On top of this, these rules help establish methods for boaters to tell each other when they’re anchored or when they’re in distress. Use your lights correctly when you need help, and you’re much more likely to get it.
When do I Need to Follow Boat Navigation Light Rules?
Light rules apply any time between sunset and sunrise. They also apply any time visibility is low.
An example of this could be during foggy or rainy weather.
A more unusual example of this could be during a solar eclipse. Basically, if you feel that having the lights on will help others see you better, it’s a good idea to turn them on.
The Different Light Rules by Boat and Size
Different types of boats will have different light rules that they need to follow. These sets of rules are broken down based on whether the boat is a sailboat or a powered boat.
Once this is established, the rules are then broken down by size.
The different sizes to consider are boats shorter than 39.4 feet, boats sized between 39.4 and 65.6 feet, and boats greater than 65.6 feet.
If you’re wondering why the numbers are so precise, it’s because this is the conversion from meters. 39.4 feet equals 12 meters, and 65.6 feet equals 20 meters.
Generally, all boats will have a red light on their port side and a green light on their starboard side. To put it in plain English, if you’re in the driver’s seat, the red light goes on the left, and the green light goes on the right.
A white light should be at the stern of the boat. The stern is the rear of the boat.
Powered Boat Light Placement

Here are the lights you’ll need when operating a powered boat, depending on the size of the boat you’re operating.
- Boats less than 12 meters or 39.4 feet long:
You’ll need one red light and one green light at the front port and starboard sides of the boat for these boats. These lights should be positioned so that they can be seen at an angle of 112.5 degrees. The sidelights should be strong enough to be seen from a mile away.
You’ll also need to mount them towards the bow of the boat. This is otherwise known as the front of the boat.
Additionally, you’ll need one white light that can be seen from all angles. It should be strong enough to be seen from two miles away.
This light will need to be mounted at least 39 inches or 99 centimeters higher than the red and green lights.
- Boats greater than 12 meters or 39.4 feet but less than 20 meters or 65.6 feet:
With boats of this size, you’ll still need your red and green lights, but your white lights will change.
In this case, you’ll mount a red light to your port or left side and a green light to your starboard or right side. These lights will need to be seen from an angle of 112.5 degrees, and they’ll need to be seen from a distance of one mile.
The two white lights will need to be mounted at the stern and masthead of the boat. Stern lights can also be referred to as the aft light. Either way, it just means the light at the back of the boat.
This light will need to be seen from a 225-degree angle facing the rear. It needs to be strong enough to be seen from 2 miles away.
The masthead light is at the forward position of the boat. This light is mounted on the masthead, and it must cover a 135-degree angle.
The light will need to be visible from 2 miles away.
Masthead lights must be mounted at least 8 feet above the gunnel. The gunnel is the top edge of the side of the boat.
- Boats larger than 20 meters or 65.6 feet long:
To operate a non-commercial boat over 20 meters or 65.6 meters long, you’ll have to have the same lights in the same positions as the smaller boats. However, you’ll also need to add matt black inboard screens to your sidelights.
Sail Boats and Other Unpowered Boats

These boats can be broken down into two different size categories.
These two categories are under 23 feet or 7 meters and boats that are over 23 feet or 7 meters.
Unpowered boats such as sailboats, rowboats, and kayaks under 23 feet in length only need to have a white light on them. This white light can be anything from a flashlight to a lantern.
However, you can still opt to place red and green lights at their appropriate places.
Larger sailboats will need to have a 135 degree white light at the stern and 112.5 degree red and green lights at the port and starboard sides. The white light should be visible from 2 miles away, while the red and green lights should be visible from 1 mile away.
Alternatively, a tri-color light could be placed on the masthead.
This light will have all three lights built into it, and it should be visible from at least 2 miles away.
Advice For All Boats Regarding Light
Regardless of what boat size you’re on, it is a good idea to have a flashlight with you.
If your boat lights become inoperable, you’ll at least have one light that you can signal with.
Should you find yourself on the water at night in a disabled boat , your flashlight may be the only thing keeping you from being crashed into.
Light Rules For Boats at Anchor
When you’re anchored at a marina or dock, you won’t have to worry about specific boat light rules and regulations.
However, when you’re anchored out on the water, you must follow boat light rules as this will help keep other boaters from running into you.
It will also help establish that you have the right of way so you won’t have to move every time a larger boat comes your way.
Of course, having the right lights doesn’t mean you’ll be able to anchor just anywhere. You’ll still have to follow any inland rules when it comes to anchoring your boat.
When anchored, you’ll need to display an all-around white light that lets other boaters know your position. This light should be placed where other boaters can best see it. For example, a sailboat might put this light at the top of its mast. Also, another all-around white light might be placed near the deck to help identify your anchored boat to nearby boats.
Boats Under Distress
Boats under distress should display what is known as a visual distress signal so that they can get help. At night, these distress signals will come in flares, parachute flares, and lights.
You should have at least three devices on your boat to use for signaling.
This could come in a variety of forms, and you can use the same one three times. For example, your three devices could be having three signaling flares with you.
Only use these lights when you’re in danger. Failure to do so can result in heavy fines and potential imprisonment.
Determining Who Has The Right of Way
When you come across another boat, and you can only see a white light, then you’ll know that you’re either approaching an anchored vessel or a vessel that is moving in front of you. In this case, you can overtake them and go around them from either side.
If you come across a green light and a white light, then you have the right of way. In boating terms, this means that you are the stand-on vessel.
Technically speaking, the other boat should give way, and you won’t have to worry about changing your course.
However, there is always a chance that the other person will not give way for some reason, and you should be ready to move. You never know, the other boater may not see you, or they may not know the rules as they should. Remember, being right won’t mean anything if you end up dead in a boat crash.
If you come across a red and white light, you are the one that needs to give way. In this case, you’ll want to slow your boat down and pass by them, probably behind their path.
In all of these scenarios I described, you were in a powered vessel, and you were passing a powered boat or a sailboat that was driving while under power.
However, what happens when you encounter a sailboat or other unpowered vessel in a powered vessel?
In this case, you’ll see a red light, a green light, or a white light, but you won’t see all three. Regardless of what you see, you’ll want to give way. This is because these boats can’t maneuver as well as you, and they probably won’t be able to get out of your way before you come across them.
At this point, you can see why different boats need different types of lights and why it’s important to use the lights that apply to your particular craft. Use the wrong lights, and you’ll confuse the other boaters around you. This could easily lead to an accident that could have easily been avoided.
What About Boaters Who Are Color Blind?
Unfortunately, people who are color blind won’t safely operate a boat at night by themselves.
Also, they won’t be able to get a captain’s license as you need to pass a color blind test to get this license. Here’s an article we wrote about all you need to know about boat license types (with prices) .
If you’d like to do some recreational boating at night, but you can’t differentiate between the colors red and green, you might want to consider bringing a friend along.
This way, your friend can tell you what colors you’re coming up on so that you can safely navigate yourself past other boats.
4 Types of Boat Lights
- The red and green lights that go on the sides of a boat are known as sidelights.
- White lights that only face backward are known as stern lights, and white lights that face forward are known as masthead lights.
- An all-round white light is a white light that faces 360 degrees. These lights are used on smaller boats and on boats that are at anchor. They can be replaced by making use of a stern light and a masthead light.
- Another type of light is the tri-color light. A tri-color light can be used on a sailboat to portray the white, green, and red lights. Bi-color lights are also available for small powered boats and sailboats. These lights display both red and green light.
The combination of lights that are displayed will always give the boater a 360-degree field of light.
This ensures that other boaters can see them no matter where they are in relation to each other.
Safety Precautions To Be Aware Of
Even new boats can have lights that weren’t configured correctly or lights that don’t work.
It’s important that you check these lights before you head out on the water.
This is true even if you don’t intend on staying out after dark. After all, it’s always possible that you could become stranded until after dark or that it could become too foggy to operate out on the water without lights.
Other Things You Should Know About Boating At Night
Boat navigational light rules are critical for nighttime boating, but there are other things to consider as well.
One thing to consider when boating at night is the use of a lookout.
Having one of your passengers act as a lookout will make it more likely that you’ll spot problems in advance.
Remember, other boaters aren’t the only potential hazards you can run into at night. Shallow shipwrecks, low water depths, and unlit piers, docks, and jetties can also become hazards if they aren’t noticed in time for you to avoid them.
High beams should be used for docking purposes only. This is because using them while on the water can confuse other boaters.
Also, the high beams can shine into other sailor’s eyes and can give them night blindness.
Just think about it this way.
It isn’t safe to drive towards another car with your high beams on, so why would it be safe to drive towards another boat with high beams on?
Driving Speed
Nighttime boating should be done at slower speeds than day time boating. The primary reason for this is that visibility is more limited at night.
Driving slower will help to give you more time to react to boaters and other hazards.
When you first start boating, you’ll still have to take a moment to think about the lights you see. Driving at a slower speed will give you this additional time without affecting your safety.
Not All Lights On The Water Are Boats!
I’ll end this post with a funny story I once heard about a boat traveling at night. This story has changed many times over the years, but the gist of it’s still the same.
It goes like this:
A large vessel was traveling at night when they came across a white light in front of them. The ship captain immediately got on the radio and contacted the other vessel to demand that they get out of the way.
The other vessel responded by telling the captain to change his course. To this, the captain responded with, “This is the warship, the USS Enterprise, and I demand you change course, or we’ll be forced to take action!”.
To this, the other vessel responded with, “This is a lighthouse, and you are on course to become shipwrecked.”.
This isn’t a real story, and now that you know proper boat navigation light rules, it is a story that could never happen to you.
If you came across a white light and thought it was a boat, you’d assume it was unpowered or at anchor, and you’d take steps to go around it.
Click to share...

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: 5a987c51-705f-11ef-9434-cf35f185c17d
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.

Navigation Lights
- You are required to display the appropriate lights at night or during times of reduced visibility.
Navigation lights are used to prevent collisions at night or in times of reduced visibility, and are an essential tool in keeping you and your vessel safe. Nav lights allow you to see other nearby vessels, and allow other vessels to see you.
Nav lights also provide information about the size, activity, and direction of travel. By understanding the characteristics of Nav lights, you can determine an appropriate course of action as you approach another vessel.
On any vessel, navigation lights have a specific color, (white, red, green, yellow, blue), arc of illumination, range of visibility, and location, as required by law and regulations. For the purposes of this course, we will concentrate on pleasure boats under 65 feet in length. Knowledge of navigation lights is important to a small-boat skipper for separate, but important, reasons.
- You are legally responsible for displaying lights of the proper color, intensity, location and visibility on your boat.
- Knowing the type and heading of another boat.
Legal Requirements
Vessels are required to show the proper navigation lights from sunset to sunrise in all weather conditions, good and bad. During these times, no other lights that could be mistaken for lights specified in the Rules of the Road can be displayed, nor any lights that impair the visibility or distinctive character of navigation lights, or interfere with the keeping of a proper lookout. The Rules also state that navigation lights must be shown in conditions of reduced visibility, and may be shown at other times considered necessary.
It's Your Responsibility
It is the responsibility of the owner/operator of a vessel that she show the proper navigation lights for her size and the waters in which she is operating. It is not the responsibility of the manufacturer, importer, or selling dealer. Many boats are delivered with lights that do not meet legal requirements with respect to technical characteristics or placement on the vessel. Remember also, that the angles of visibility must be met when the boat is underway-if your boat rides at a significant bow-up angle, take that into consideration when installing and/or checking your lights.
Navigation Lights for Powerboats
Power driven vessels underway shall exhibit a masthead light forward, sidelights and a stern light. Vessels less than 12 meters in length may exhibit an all around white light and side lights. Power driven boats on the Great Lakes may carry an all around white light in stead of a second masthead light and stern light combination.

Sidelights - Colored lights - red on port and green on starboard - showing an unbroken arc of the horizon of 112.5 degrees, from dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on each side.
Combination lights - Sidelights may be combined in a single fixture carried at the centerline of the vessel.
Stern light - A white light showing over an unbroken arc of the horizon of 135 degrees, centered on dead astern.
Navigation Lights for Sailing

A sailing vessel of less than 7 meters in length shall, if practicable, exhibit regular navigation lights, but if not practical, she shall have ready at hand an electric torch or lantern showing a white light which shall be exhibited in sufficient time to prevent collision.
Diving Lights
Another light display that you may see in resort areas, or waters that have wrecks or reefs, is the night diving configuration. This has three vertical masthead lights, that have a red-white-red sequence. You must maintain a good distance from these vessels, and you should also be aware that there may be divers near you.
Interpreting what you see

It's great that you're learning the basics of lights - what is required and when they're required. But, this in only the beginning. You must also learn how to interpret the navigation lights that you see when you are underway at night- and for your safety-learn it well.
For instance, if you see a vessel approaching that shows a light pattern such as the ones to the right, you immediately know that you are in a crossing situation, and that you must yield to the other vessel - that's why it is red.

Seeing a green light over a white light indicates a fishing vessel actively trawling. You not only need to avoid the vessel, but you also need to remember that it could potentially have a very large net deployed that you will also need to avoid.
And there are numerous other lights and combinations of lights that you must be able to instantly recognize - the lights for a sailboat that is privileged over a motorboat, the special lights of various fishing vessels, a dredge or a vessel not under command. Study the requirements for navigation from the viewpoint of a "looker" as well as a boat owner.

Boat Navigation Lights: Everything You NEED to Know (2024)
In many cases, boating at night requires the use of boat navigation lights, but boaters often have many questions about them.
They often wonder when they’re needed, what the requirements are for various locations and vessels, and more.
We’re going to do a deep dive into navigation lights for boat to see what you need on your boat, and when you need to use them.
Legal Requirements
Types of navigational lights, which navigation lights are required on my boat , operators responsibility , navigation lights .
On any vessel operating on or in US waters, there is a need for the operator to display navigation lights under certain circumstances. Their purpose is to make vessels aware of each other at night or in times of generally reduced visibility. This is incredibly important during times when you may not be able to see the craft itself.
Other than visibility, marine nav lights also help boat operators determine the size, direction of travel, and even the potential activity of another boat on the water. When an operator understands the type of information each light tells them, they will be better able to determine appropriate courses of action for potential situations.
Boat running lights are divided by location and color, and each of them has specific requirements with how they must be displayed and perceived. You are the one legally responsible for displaying proper nav lights on the boat, for displaying them at the proper times, and for understanding how to read them.
The US Coast Guard ’s legal navigation light requirements include guidelines for every aspect of light usage.
Their materials start by first defining the standard daily period during which they must be used, then they detail how many of each type of light is needed as well as where they are located. Each light also has constraints regarding its visible distance and the arc over which it can be seen.
In the US, the Coast Guard says that any powered vessel that is under 39.4ft., may operate with boat nav lights in as little as two positions, an all-round light at the stern, and a set of sidelights at the bow.
Vessels that are under 164ft. must have lights displayed in four positions, a stern light, a masthead light, and boat sidelights on both the port and starboard, near the bow.
The ship navigation lights also have minimum visibility distances, depending on the size of the craft. The minimum visibility for nav lights, even for small crafts, is one mile, with requirements that other lights on larger vessels be visible for up to 3 nautical miles.
Also read: Boating Rules and Etiquette On the Water
Boat lights come in 4 types, sidelights, stern light, masthead light, and all-round light. Lights only come in white, red, and green, and all have very specific jobs.
| White | Over fore and aft centerline of the boat | 2 miles | 5 miles | 225 degrees | |
| Red | On the port side, 22.5 degrees abaft the beam | 1 mile | 2 miles | 112.5 degrees | |
| Green | On the starboard side, 22.5 degrees abaft the beam | 1 mile | 2 miles | 112.5 degrees | |
| White | Near as possible to the stern | 2 miles | 2 miles | 135 degrees | |
| White, Yellow, Tricolor | N/A | 2 miles | 2 miles | 360 degrees | |
| Green, Red, White | Over fore and aft centerline of the boat | N/A | N/A | 360 degrees | |
| Two White Vertical, Three White Vertical | Over fore and aft centerline of the boat | 2 miles | 2 miles | 135 degrees | |
| Flashing Blue | Anywhere not interfering with other lights | 2 miles | N/A | 180-225 degrees |
Masthead Light
The masthead light is the white light located about ⅔ of the way up the mast, rather than at the top as you’d think. This boat bow light is required when using motor power at night. To be acceptable, the light must have an arc of 225° and needs to be seen from 2 miles away.
Large boats can have up to 3 mast lights. If your boat is shorter than 39 ft., all 2-3 white mast lights can be combined, utilizing one larger white light at the top of the mast.
Color : White ARC : 225 degrees Position : Front of boat
Port Sidelight
The boating lights located on the port side of the watercraft are red and mounted so that boats can see as they approach either head-on or from the left. This light helps tell if a boat is coming towards you or if it is pointing away. The phrase “red, right, returning” means that if you see a boat with their red navigation light on the right, they are facing your boat. The only time it is not needed is when your boat is anchored for the night .
Color : Red ARC : 122.5 degrees Position : Forward, left side
Starboard Sidelight
If you are to approach a boat from the front or right, you will see the green starboard sidelight. With an ARC of 122.5 degrees, approaching boats will be able to see yours easily.
This light helps tell you whether or not you have the right of way, which is important when it comes to keeping both you and your passengers safe. These are some of the front boat lights.
This light will often be combined with the port light, in small boat navigation lights. When out in the water, if you see the green light, that means it is safe for you to go, as you have the right of way.
Color : Green ARC : 122.5 degrees Position : Forward, right side.
The rear boat light is called the stern light. It is used to mark the rear of the boat. The operator can infer from only setting a boat stern light, that they are directly behind the vessel.
The stern light is white and is visible for an arc of 112.5 degrees on both the port and starboard sides, making a full arc of 225. Being able to see the red starboard side light as well as the stern light, should indicate the other vessel is traveling to the right from the perspective of the observer.
Color : White ARC : 225 degrees Position : Stern
All-Around Light
One of the boat night lights that is required when on your boat between sunset and sunrise is the all-around light. This light is intended to be seen from any point and helps to tell what direction a boat is moving. This light is also used when a boat is stopped or anchored.
This anchor light is required to have an ARC of 360 degrees and should be visible for two miles. The all-around light is white and it is located at the top of your boat’s mast for maximum visibility.
Color : White ARC : 360 degrees Position : Top of mast
Tricolor Light
A tricolor light is a sailboat mast light that has your three types of bow light in one convenient piece of equipment. They are for sailboats that are smaller than 65.6 feet long. The point of this sailboat light is to increase your nighttime visibility. They are mounted at the top of the mast, allowing larger boats to see yours better. They are not permitted to be used by any boats with a motor. The only type of boat that can utilize a tricolor light is a sailboat.
Color : White, red, green ARC : 360 degrees Position : Top of mast
Towing Light
These yellow lights are important, as they indicate to other watercraft that, not only is there another boat nearby but that they are also towing someone as well. The light must be positioned at the back of the boat, as close to the stern as possible. The goal is to avoid having anyone run into the boat that is being towed, as there may be no lights showing where that boat is located. The boat lighting requirements when towing state that both sidelights, a stern light, and masthead lights should also be displayed.
Color : Yellow ARC : 135 degrees Position : Over fore and aft centerline of the boat
Law Enforcement Light
Lights used by law enforcement on the water are flashing blue lights that can flash 120 times per minute or more. They can be used nearly anywhere that is convenient for the operator, provided they do not interfere with the function of the other lights.
This light may be displayed by any type of local law enforcement that is engaged in the course of their duty. This can apply to local, state, or federal police, as well as officials from wildlife and conservation departments, the Coast Guard, and more.
Color : Flashing Blue ARC : 180-225 degrees Position : Anywhere not interfering with other lights
Find your boat type below for the lineup of nav lights that you will need to safely operate after sunset and in other times of limited visibility.
Be sure you know which lights you will need to have on while underway, as well as at anchor or while towing. If you’re sailing, don’t forget that you are considered power-driven when using your motor.
Powerboat under 23 feet (7m)
Powerboats under 23 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- One white masthead light visible for 2 miles
- One red & green sidelight visible for 1 mile
- One stern light visible for 2 miles
- One white, red, green, or yellow all-round light visible for 2 miles
Powerboat Under 39,4 feet (12m)
Powerboats under 39,4 feet are required to follow these boat light rules:
- One all-round light visible for 2 miles
Powerboat Over 39,4 feet (12m)
Powerboats over 39,4 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- One white masthead light visible for 5 miles, unless less than 20 meters, then 3 miles
- One red & green sidelight visible for 2 miles
Powerboat 39,4 feet (12m) to 164 feet (50m)
Powerboats between 39,4 feet and 164 feet are required to have the following marine running lights displayed:
- One white masthead light visible for 6 miles
- One red & green sidelight visible for 3 miles
- One stern light visible for 3 miles
- One all-round light visible for 3 miles
Sailboat Under 23 feet (7m)
Sailboats under 23 feet are required to have the following sailing navigation lights displayed:
- One white stern light
- One white mast lantern positioned at or near the top of the mast where it can be easily seen from a distance
Note: if it is not practicable for the vessel to display the prescribed lights, one all-round white light can be used or a hand torch, with enough time to prevent a collision.
Sailboat Under 65,6 feet (20m)
Sailboats under 65,6 feet are required to have the following sailing lights displayed:
Tug Boat With Tow Length Under 656 feet (200m)
Tug boats with tow lengths less than 656 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- Two masthead lights in a vertical line
- Stern light
- Towing light in a vertical line above the stern light
Tug Boat With Tow Length Over 656 feet (200m)
Tug boats with tow lengths longer than 656 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- Three masthead lights in a vertical line
- A towing light placed vertically above the stern light
- A diamond shape visibly displayed
Anchored Vessel
Vessels at anchor or aground are required to observe the following boat lighting rules:
- One white all-round in the fore
- One white all-round at a lower level than the fore, at the stern
If aground, the vessel should display two red all-round lights in a vertical line
Vessel Under Oars
Vessels under oar power have similar requirements to follow as small sailboat lighting:
- One stern light
Or, alternately, one white all-round light or hand torch to be used to manually signal to avoid collision
Vessel Engaged in Fishing
Vessels actively engaged in fishing are required to have the following marine navigation lights displayed:
- Two all-round lights oriented in a vertical line, red on top and white on the bottom
- One all-round white light for gear more than 150 meters from the vessel
- When making its way through the water, there shall also be sidelights and stern light
Vessel Engaged in Trawling
Vessels engaged in trawling are required to fulfill the following boat light requirements:
- Two all-round lights oriented in a vertical line, green on top and white on the bottom
- One masthead light abaft and higher than the all-round green
Kayakers and Canoers
Kayakers and canoers are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
Alternatively, a hand torch or lantern which can be used to signal to avoid collisions
Personal Watercraft
There are no established rules for navigation lights on personal watercraft, even though many of them are classified as a boat by coast guard standards. Personal watercraft are often not permitted to operate outside of the sunrise-to-sunset period, and so most manufacturers do not install or make possible the installation of navigation lights.
Vessels Restricted in their Ability to Maneuver
Vessels restricted in their ability to maneuver are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- Three all-round lights displayed as high a possible in a vertical line, red at the top, and white in the middle
- One masthead light
The USCG as well as state authorities hold the operator of the vessel responsible for the correct use and understanding of nav lights.
This means they also must make sure all of the lights used meet the requirements set forth by the authorities.
This also extends to ensuring that the lights are all installed for optimal visibility while underway, so if your cruiser rides high, make sure your lights are still visible.
What navigation lights do I need on my boat?
Boat light regulations state boats must have a pair of red and green sidelights, and an all-around white light that can be seen from 360°.
Why are navigation lights red and green?
Navigation lights for boats indicate to others which direction a boat is facing. The red indicates the left side of the boat, green is on the right.
What lights need to be on a boat at night?
Per the navigation lighting rules, it is crucial that you have your red and green navigation lights, as well as the white 360° light.
Which three colors are used for navigational lights?
The boat light colors are going to be green, red, and white. If you see a blue light, this generally indicates a government vessel.
Do I need navigational lights on my boat?
Yes, all boats are legally required to have the minimum red, green, and white boat safety lights
when operating in the dark.
Why do boats have blue lights?
When you see a boat that has blue boat lights at night, that means that it is likely the coast guard or law enforcement.
Why is port red and starboard green?
The light on the starboard side of the boat is green because it is ‘safe’, as the steersman will be able to see other boats.
What does a single white light mean on a boat at night?
If you can only see a single white light on a boat at nighttime, you are likely seeing the stern light or the boat anchor light.

Robert Owens is the Chief of Content of Quicknav. Robert has been boating for over ten years and loves to share his experience on the water. His first boat was a dirt-cheap moderately beat up 2003 Bayliner 175, where he learned a tremendous amount about trailering, launching, docking, operating, and maintaining. He currently owns a Cruiser Yacht and is eyeing a sailboat.
Similar Posts

How Much Does a Boat Cost in 2024? (With Ownership Costs)
Residents all across the US are buying more boats than ever before. From kayaks and canoes to the most luxurious…

Boat Steering Systems: Everything You Need to Know (2024)
One of the most important tasks in your yearly boat maintenance routine will be the inspection and potential repair of…

Glossary of GPS Terms in 2024 (The Definitive List)
Learning about global positioning systems or GPS can lead you down a rabbit hole of technical material, many dealing with…

12 Practical Tips to Learn Boating Fast (2024)
For someone who wants to learn boating, it can be a bit intimidating looking from the outside in. You might…

How to Get a Marine Radio Operator Permit in 2024?
Obtaining your marine radio operator permit from the FCC is only a necessity under certain circumstances (1), but they allow…

Boating Statistics in 2024 (incl. Covid & Millennials)
It’s no secret that Americans love boating as boating and fishing are the largest outdoor recreation activities in the U.S….
- Members Forum
- Log In / Create Account
Navigation Lights at Night
by Harbor Sailboats | Dec 4, 2020 | Blog | 1 comment

Great article! Boat lights are the means of communication between sailing vessels. These lights are also a tool to let my presence known even from a distance.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Latest Blog Posts
- Talk and Walk
- Sailing Lessons in San Diego
- Water in the Bilge
- Bow Standing
- Gear then Steer
Boat Reviews
- Boats Specs
- Marine Pros
- Boat Insurance
- Boat Warranties
- Boat Transport
- Boat Towing
- Marine Forecasts

Your Ultimate Boating Resource

What are the proper sailboat lights at night?
As a sailor, it is essential to be aware of and adhere to proper sailboat lighting when navigating at night. These lights are necessary to ensure safety and avoid collisions with other vessels.
The International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGS) specifies lighting requirements for different types of boats. There are different lighting rules for vessels under power and those under sail. In this article, we’ll discuss the proper sailboat lights at night.
Sailboats are required to have three lights at a minimum: a masthead light, a red port light, and a green starboard light. The masthead light is white and is located at the top of the mast. This light should shine forward and aft and be visible from 2 nautical miles away. It is important to ensure that the masthead light is not obstructed by the sail or any other structure onboard.
The red port light is located on the left or port side of the boat and is visible from 1 nautical mile away. The green starboard light is on the right or starboard side and is also visible from 1 nautical mile away. These lights should shine out from the vessel and be visible from dead ahead to 112.5 degrees abaft the beam on either side.
In addition to these lights, sailboats that are underway may show an optional stern light. This light is placed at the stern of the vessel and is white. It should be visible from 2 nautical miles away and can be used to indicate that the sailboat is underway and not at anchor.
If a sailboat is not underway but still poses a potential hazard, it should display an anchor light. This is a white light that is visible from 2 nautical miles away and should be located near the top of the mast. This light indicates that the sailboat is anchored and should be avoided by other vessels.
It is important to note that the visibility of the lights depends on the weather and other conditions. In foggy or hazy conditions, the lights may not be visible from the specified distance. It is always a good idea to maintain a lookout and be aware of other vessels in the vicinity.
Proper sailboat lighting at night is critical to ensuring safety and avoiding collisions with other boats. It is essential to understand the required lighting regulations and to ensure that all lights are functioning correctly before heading out on the water. Remember to always maintain a lookout and be aware of other vessels around you. Happy sailing!
Related Questions
What type of wood is used for pier pilings, what is the difference between a dock and a floating pier, what is the proper technique for pulling a beginner wakeboarder, what does ‘no wake’ mean on a lake, what is the difference between wash and wake, is wakesurfing possible in the sea, why don’t wooden piers rot, what size wakeboard is needed, how to achieve more pop on a wakeboard, does wake surfing translate to ocean surfing, latest posts, overview of the 2024 sea-doo rxp-x 325, overview of the 2024 parker offshore 2900 cc, what your boat’s beam is and why it matters, power cats of 2024: ultimate guide to the top power catamarans this year, don't miss, our newsletter.
Get the latest boating tips, fishing resources and featured products in your email from BoatingWorld.com!
Navigating the Heat: 10 Safety Tips for a Safe Boat Ride in the Summer Heat
Highs, lows, and tidal know-how: a deep dive into ocean currents, 10 essential tips for fishing near private property, the benefits of using a drift sock: guidance for anglers, lure fishing: secrets for imitating live bait and attracting fish, explore the untapped depths of america’s best bass fishing spots, outboard motor maintenance: tips for keeping your engine in top shape, the essential boat tool kit: tools every boater needs, diy boat building: 8 tips and tricks for building your own vessel, the art of miniature maritime craftsmanship: ship in a bottle, antifouling paints: a guide to keeping your boat shipshape, beginner’s guide to standup paddle boarding: tips and techniques, boating for fitness: how to stay active on the water, kayak safety: how to stay safe on the water, anchoring in a kayak or canoe: how to secure your small boat, overview of the 2024 yamaha 252sd, overview of the 2024 tiara yachts 48 le, overview of the 2024 bass cat jaguar sts, 2024 pursuit os 445: an overview, 2024 aquila 47 molokai review, 2024 sea-doo switch 13 sport review, gear reviews, megabass oneten max lbo jerkbait review, fortress anchors fx-7 anchoring system review, fortress anchors fx-11 anchoring system review, fortress anchors commando anchor kit review, fortress anchors aluminum anchors review, stay in touch.
To be updated with all the latest news, offers and special announcements.
- Privacy Policy
Get your card today

- Pre-paid code

- Buy a Gift Card
Boat Navigation Light Rules and Requirements
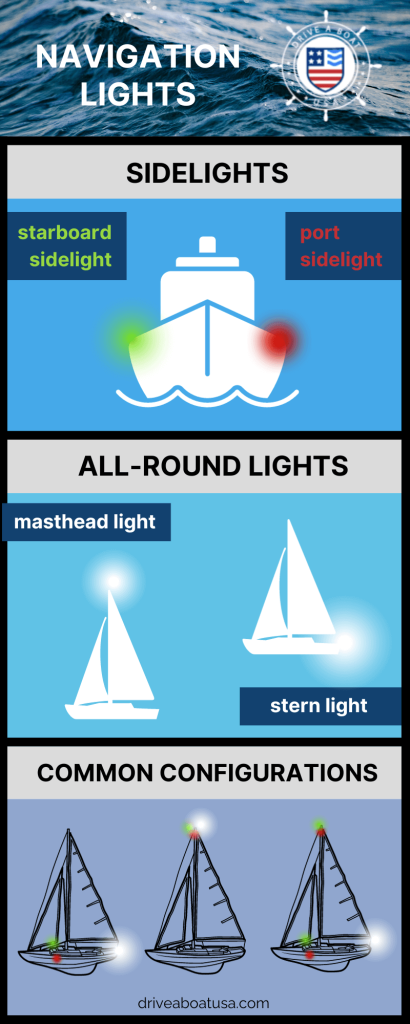
Boat navigation lights are one of the most important pieces of safety equipment on your boat, along with personal flotation devices , boat fire extinguishers and boat ventilation systems .
As a boat owner or operator, you are legally responsible for using the correct safety equipment at all times. This is your responsibility whether your boat is moving through the water or you are at anchor, day and night, in all types of weather.
Did you know that boat manufacturers, importers and dealers are not responsible for equipping your boat with legally acceptable navigation lights ? Before you take to the water, check that your navigation lights are:
- the right size and type for your boat and chosen water activity
- the right color and intensity
- attached to the correct parts of your boat
- fully operational.
It’s important to learn all you can about navigation lights for safe, legal boating! Keep reading to find out which lights to use when.
What are navigation lights for?
Navigation lights allow you to see and identify other vessels, and allow other boats to see and identify you. There is not one simple way to use navigation lights; the way they are set up on your boat will indicate the size, activity, and direction of travel of your vessel, so that you and other boat operators can make good decisions and avoid collisions.
By understanding what navigation lights mean, you will be able to safely and legally navigate shared waters under a variety of circumstances.
Boat navigation light requirements
Paddleboats, rowboats and small sailboats generally do not need to display navigation lights, but most other boats are legally required to use some or all of the following:
- A green light to indicate the starboard (starboard sidelight) attached near the bow on the starboard side
- A red light to indicate the port (port sidelight) attached near the bow on the port side
- One or more white lights (stern light and masthead light)
- Other navigation lights , such as blue flashing lights for law enforcement vessels engaged in search-and-rescue (SAR) operations, or yellow lights for vessels that are towing or being towed
Each type of navigation light also has a defined arc of illumination and range of visibility. Angles of visibility must be met when the boat is underway, which means that if your boat rides at a significant bow-up angle, you may need to adjust your navigation lights to compensate.
You must always use navigation lights between sunset and sunrise or in reduced visibility, but there are some exceptions during clear, daytime boating.
Note: It is also important to keep a flashlight on board as a temporary replacement, in case a navigation light burns out.
Boat navigation lights while underway
While your boat is underway, you are legally responsible for displaying the right type of navigation lights. Choosing the right lights depends on several factors, including:
- Whether your boat is powered by an engine (in full or in part)
- The size of your boat , measured in length
- Your boat’s speed
- Where you are boating (inland, international water, etc.)
- Whether you are at anchor.
Remember that your navigation lights must be visible and easily identifiable as such. Other lights on your boat cannot be mistaken for navigation lights, or get in the way of your navigation lights
Sailboat navigation lights
If you are operating a sailboat or nonpowered boat such as a canoe, kayak or rowboat, you still need to use the correct configuration of navigation lights for your boat size and boating circumstances. For comprehensive detailed instructions on navigation lights please refer to the USCG resource. The following are general guidelines:
Sailboats or vessels using paddles or oars, under 23 feet in length:
- One white navigation light (or lantern or flashlight) that is visible from 2 nautical miles away between sunset and sunrise or during periods of low visibility. In the presence of another vessel, the light must be displayed in time to avoid a collision.
Sailboats between 23 and 65.6 feet:
- One white stern light visible at 135 degrees and from 2 nautical miles
- One green starboard and one red port sidelight, visible across 112.5 degrees from one nautical mile away
- A tricolour light, which is a single all-around light which includes the three coloured of lights indicated above, facing the same directions, visible from a distance of 2 nautical miles. This type of light can only be used when under sail, and never when using a motor regardless of whether the sails are hoisted. It may not be used at the same time as regular sidelights.
Powered boat navigation lights
If you are operating a boat with an engine (including sailboats with motors), between sunset and sunrise or under conditions of restricted visibility, you need navigation lights.
Powered boats under 39.4 feet:
- One all-around white light, visible from all directions (360 degrees) from two nautical miles away. This light must be attached at least 39 inches above the sidelights.
Recreational powered boats between 40 feet and 164 feet:
This size of boat requires two white lights which, combined, make up 360 degrees of visibility:
- A white masthead light at the bow, visible across 225 degrees, from 2 nautical miles away. This light must be attached at least 8 feet above the gunnel.
- A white stern light at the stern, visible across 135 degrees and from 2 nautical miles away.
In addition to:
- One green starboard and one red port sidelight, visible across 112.5 degrees from one nautical mile away.
Boat navigation lights at anchor
When your boat is anchored at a dock, it is not necessary to turn on your navigation lights. However, if you are at anchor in an undesignated area, you need to make other boats aware that you are not moving by displaying an all-around white light where it will be easily visible to any other boats in the area.
Diving lights
If you are boating in a resort area or anywhere there are sunken wrecks or coral reefs, keep in mind that there could be diving activity. Keep your distance and stay alert to the possible presence of divers underwater.
Boats that are accompanying divers must display:
- Three vertical masthead lights in a red-white sequence.
Interpreting boat navigation lights
Installing and using the right navigation lights on your boat is very important, but to navigate safely, you also need to be able to interpret the navigation lights on other boats.
Remember, you may not always be boating under ideal circumstances. Make sure you learn to understand navigation lights and the United States Coast Guard rules of navigation , also called the Rules of the Road , thoroughly, so that you can make good decisions quickly, as needed.
Do you see a green light over a white light? This indicates a fishing vessel that is actively trawling. It may be necessary to avoid not only the boat, but also a large net.
Do you see a red light to the left, with two white lights to the right? Understand that you must yield to the other boat.
There are many other configurations you need to be familiar with to operate your boat safely.
Avoiding collisions
Remember, navigation lights are only a tool. You must also maintain a proper look-out at all times, by sight and hearing, to responsibly avoid collisions. Skippers must drive at an appropriate speed so that you can take effective action to avoid colliding with another vessel or body under or on the water.
Factors like visibility, traffic density, the maneuverability of your vessel, the presence of other lights from shore or scattered boat lights, the state of the sea and the draft in relation to the available depth of water must always be taken into consideration. Radar equipment may also pose certain limitations or offer certain benefits to navigating safely.
It is the boat operator’s responsibility to do everything in their power to avoid a collision, including but not limited to the correct display of navigation lights.
Learn about boat navigation and more from Drive A Boat USA!
Driving a boat safely demands a thorough knowledge of navigation, safety procedures and other technical details.
What you need to know depends in part on where you intend to go boating, the size and type of boat you will use, and what type of activity you will be engaged in, but there are many basic rules and regulations that you are legally obliged to follow no matter what the circumstances.
You can get your official state-approved online boating license today! Sign up for our fun and engaging boating safety course to get started.
- USA Boating
Latest Posts
- Everything You Need to Know About Safe Boating with Dogs
- All About Vessel Safety Checks (VSC) in the U.S.
- Common Causes of Boat Fires
- Tips and Tricks for Docking Your Boat
- Diver Down Flag: What It Looks Like and When To Use It
- August 2024
- February 2024
- December 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- January 2023
- November 2022
- Get certified now
- Replacement California Boater Card

Navigation Lights for Sailboats (And How To Read Them)

Navigation lights on a sailboat can be confusing. If you understand the reason behind why they are the way they are however, they can make a lot more sense.
At their heart, sailboats are really just a power boat and as such must adhere to all power boat rules such as navigation lights. Other times however, a sailboat is classified in a special category. They have a set of additional lights they CAN show as an option, but are not always required to do so.
That’s about as clear as mud if you ask me and I contend that that is where the confusion about lighting a sailboat begins.
Just because you can show a light to identify yourself in times of low visibility, does not mean you have to and then we add in a little sibling rivalry between power and sail and things get downright adversarial when it comes to navigation and the night.
Table of contents
The USCG says You’re a Power Boat Whether You Like It or Not
Much to the consternation of many a sailor who has earned a commercial license to drive their sailboat, when you received your credential from the USCG it says you are a master of steam and power across the top with no mention of wind as a source of propulsion.
It is not until you read the back pages of your little red book that feels like a passport and looks like a US Sailing credential, that you will see the term “sail auxiliary”. That is because most of the time the U.S. Coast Guard knows that you are primarily reliant on your mechanical power to propel your vessel.
It's a sad thing, but the days of commercially viable sail boats are done and all but the most select few even have sails let alone use them as their primary power source. All sail boats by law are powerboats, but not all powerboats are sailboats.
Navigation Lights for a Power Boat
As a power boat, you are required to show certain lights and have been required to do so before power was even invented.
In the days of man powered vessels like the viking ships who relied on oars while in close quarters to power their vessels, they needed to show other boats, friend or foe, where they were by showing lanterns in the dark to identify themselves. As you know, it is a time honored rule among all the nations of the world both past and present, that you must avoid a collision at all costs while at sea and even the viking knew that you should not run into things.
By lighting the front and back of your boat, you could warn other boats of your presence as well as identify which way you were heading. As such there is a very specific rule in the Code of Federal Regulations Number 46 (CFR46 by common name) that spells out with detail how many, the color, the luminosity or brightness, the angle of visibility and the location of all of the lights required for navigation on every single boat, seaplane, submarine and other nondescript vessel conceived by man to date that they must show while underway in reduced visibility.
And there is no flexibility in the rules.
As such a power boat, and by extension all sailboats, MUST, without question show one green light on the starboard bow and one red light on the port bow and one all around white light or lights while operating in reduced visibility. These lights should shine at all 360 degrees of visibility with the bow lights shining at an angle of dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam and the stern lights shining 225 degrees dead aft. A forward facing masthead light that is white in color shall shine forward to comply with the directive that all vessels must carry an all around white light. For more read here .
As you can see, there isn’t much wiggle room when it comes to lights that must be shown.
Sailboats get a little flexibility with lights
Sailboats however, are a little different when they are in fact sailboats, which is only when you are entirely reliant on the wind for power and in no way reliant on any mechanical or manual means of propulsion. And for good reason.
Back in the day when men were men and sailboats were wooden, fire was a major concern. Sails were coated with wax and other flammable substances and the wood on boats was saturated with oils and grease. Even the ropes were plant materials saturated with oils to keep them pliable and strong.
Add those highly flammable substances to a parching environment like the sea and you had what was essentially a giant floating tinderbox.
Then tell that giant floating tinderbox that they need to identify themselves to the world at large at night using oil lamps with flames because batteries and lights were not invented yet. It didn't take very long or very many ships burning to the water line for the Governments to say to the sailboats, you get to do things a little different.
As such, sailboats are given special dispensation when it comes to lights aloft. They don't have to show an all around white light in their rigging because no one wanted to set their rig on fire with oil lamps 60 feet up in their rig.
However, when a sailboat takes their sails down such as when they are powered or at anchor, they must resume the display of an all around white light or lights aloft. That became a real challenge with aluminum masts and the disappearance of rat lines on the shrouds because there was no easy way to climb the rig and check the bulbs up the mast on a regular basis.
Red over Green Sailing Machine
I have no idea where the history of this particular light comes from, but if you ever take a deck exam with the USCG, you better remember this mnemonic. An all around red light over an all around green may be displayed on a vessel during times of reduced visibility to indicate that a vessel is operating under sail power alone.
I won’t even speculate on how or why they came up with this particular light configuration, but if you want to use these lights as a sailing vessel, you can do so, but that means that you will need three all round lights at the top of your mast, an all around white, an all around red and an all around green, just in that order.
The red over green is to be displayed in addition to the running lights or the red and green bow lights with the 225 degree stern light. As always, when the motor comes on, so does the steaming light or the forward facing white light that is also usually about ¾ of the way up on your mast to complete the requirement of an all around white light that indicates a power vessel.
What is a “steaming light” and why are you mentioning it now?
Most sailboat electrical panels will have a switch that is labelled “steaming light” and it will only come on when your anchor light is off. This is probably the most confusing part of sailboat navigation lights so if you are confused about this, you're in good company as most people are.
A “steaming” light is named thusly, going back to the days of steam powered sailboats where when they fired up their boilers and doused the sails, they became a power boat once again. There aren’t too many steam powered boats, let alone steam powered sailboats, but the name stuck and it is a vestige of a bygone era.
Either way, when you fire up your motor, you turn on your “steaming light” and that locks out the all around white light which is used for anchoring to minimize the number of switches on your panel and reduce the number of wires in your mast. The fewer wires, the less chance of something not working or becoming disconnected.
The steaming light and the anchor light both go up the mast, but you can’t use an all around white light while using the 225 degree stern light at the deck level because to other boaters you would look like you have two white lights from the stern and that would be confusing.
The anchor light is used exclusively for anchoring while the steaming light is used to indicate you are a power vessel while underway.
As to why I am mentioning it now in the article, is because this would have blown your mind if I started with this subject cause it can be really confusing stuff.
Aspect Recognition with Lights
Remember when I said earlier that lights can help you tell others which way you are heading as well as tell you which way other boats are heading? That is called the aspect of the vessel and the USCG tests you on this for your deck exam as well.
Knowing that the bow lights go 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on both sides or 112.5 degrees on each side, and the stern light faces 225 degrees aft for a total of 360 degrees of visibility, you can tell a lot about where a boat is heading and who has the right of way.
One thing that's easy to remember is red means stop and if you see a vessel's red light, it means stop as you are the give way vessel and approaching the other vessel from his port side. Conversely it works with green as well as that means you are approaching from the other vessel's starboard side and you are the standon vessel.
If you see a red and green light equally low on the horizon, that means your heading dead on into another vessel's path and conversely if all you see is a white light low on the horizon, it means you are overtaking another vessel power or sail, we don’t care because it is an overtaking situation. However, any time you do see a white light aloft in addition to the red and green bow lights, you know you are encountering a power boat.
Then there are angular approaches as well, where you see white and red or white and green light low on the horizon. You know in that case you are seeing a portion of the bow lights and stern lights from the side approaches of a vessel. Based on which direction those lights are heading, you can deduce which way that boat is going in relation to your boat.
So put it all together and you see a green light and a white light low on the horizon with a red over green light aloft, you know that you are approaching a sailboat that is traveling to your port and that might make you the standon vessel. That is of course, if we didn’t concern ourselves with windward and leeward and port tacks and starboard tacks, but that is a discussion for another article. So stay tuned when we talk about sailing rules and the right of way. But for now, do good, have fun and sail far.
Related Articles
Capt Chris German
Capt Chris German is a life long sailor and licensed captain who has taught thousands to sail over the last 20 years. In 2007, he founded a US Sailing-based community sailing school in Bridgeport, CT for inner city youth and families. When Hurricane Sandy forced him to abandon those efforts, he moved to North Carolina where he set out to share this love for broadcasting and sailing with a growing web-based television audience through The Charted Life Television Network.
by this author

Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
Daniel Wade
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

How To Drive A Pontoon Boat
Jacob Collier
December 19, 2022
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
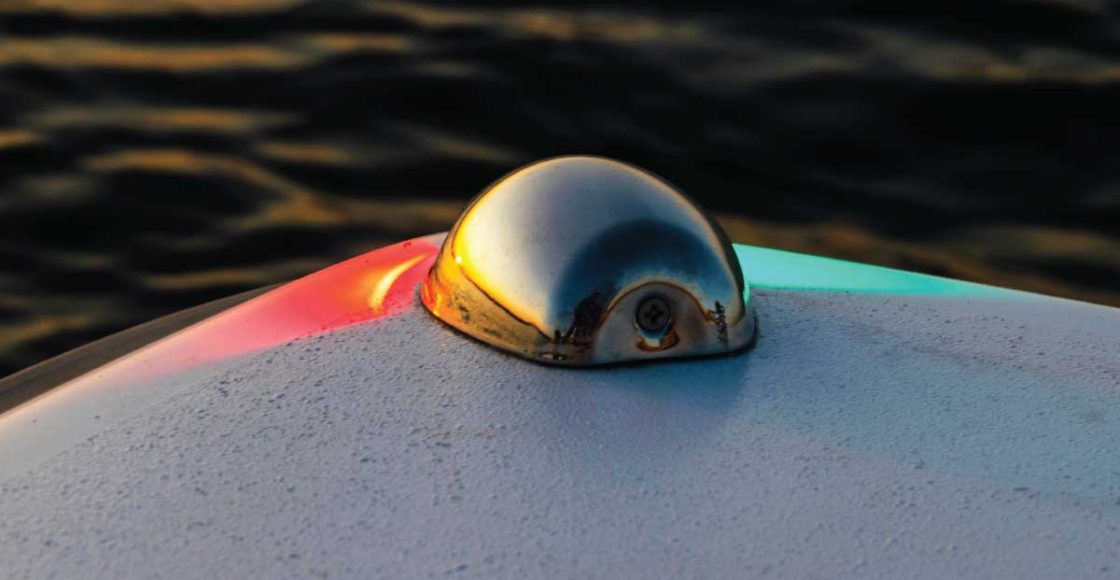

Boat Navigation Lights: Understanding the Basics

Table of Contents
Last Updated on July 19, 2022 by Boatsetter Team
For many boaters, the best way to end a beautiful day on the water is to watch the sun slowly drop below the horizon while it lights up the clouds and sky above. Others feel better heading to the dock before the sun goes down, while there is still plenty of light to illuminate the channel markers and other potential dangers.
Besides understanding boat navigation light rules, it is also important to understand:
- The overall purpose of boat navigation lights
- How to properly use boat navigation lights
- What the different colors (red and green) mean
Own a boat? Earn an avg. of $20K per season renting it out on Boatsetter
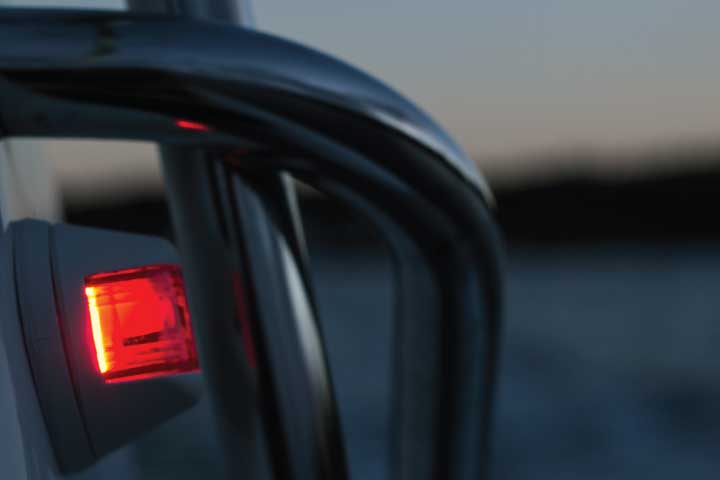

How do boat navigation lights work?
Boat navigation lights, or “nav lights,” are the colored marker lights visible on either side of the vessel and at the stern . These lights play essential roles in identifying the ship’s length, direction, and purpose!
The colored marker lights and where to find them go as follows:
- The boat’s port side is marked with a red light.
- The starboard side light is green.
- When looking at the boat’s transom or stern, a white light may be visible.
Keep in mind large boats and ships may use other colors, like yellow.
Next time you’re boating at night , say thanks to your navigation lights. They allow you to see other boaters in the dark and help prevent collisions. But there is much more to boat navigation lights than that.
How to use boat navigation lights
Each of the boat’s navigation lights is only visible for so many degrees of a circle to prevent confusion and accurately identify which side is in view.
By noting which colors are visible on another vessel, boaters can identify which direction the other boat is facing or headed. Knowing a boat’s direction can be especially important when crossing paths with another vessel in the dark.
If you walked around a boat at night while the navigation lights were on, the color visible would change depending on where you stood. When looking at the port side of the boat, the red light would be visible from dead ahead of the vessel to just past the center of the port side or through 112.5 degrees of a circle. Walk to the starboard side, and the green light would be visible from the bow to just past the boat’s center, or another 112.5 degrees.
Stand at the back of the boat, and you will see the white light visible for a total of 135 degrees from one side of the vessel to the other. Add up all three, and you’ll get 360 degrees.
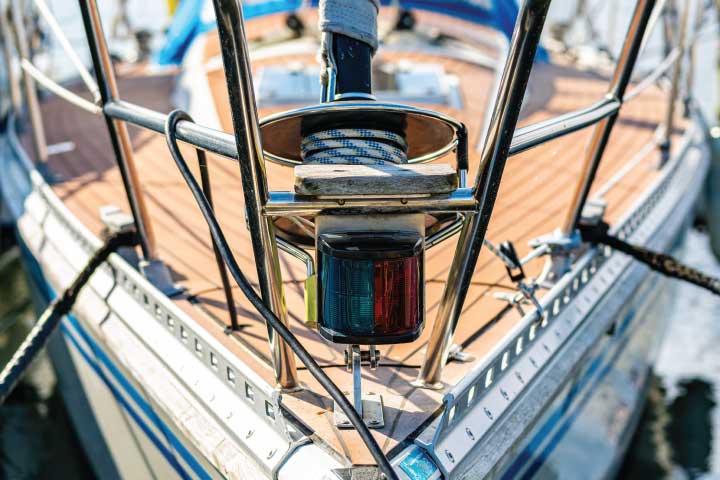

Boat navigation light color meanings
If you were on a boat at night and could see nothing but the different colored lights of another vessel ahead of you, you would still know exactly which way that boat was going.
- If you could only see the red light ahead of you, you would know that you are seeing the other vessel’s port side, or it is crossing in front of you from your right to left.
- The opposite is true if you saw the other vessel’s green light . You would be looking at the other vessel’s starboard side or watching the boat pass in front of you from left to right.
- If you see both red and green lights , then the other vessel is coming straight at you if you can see both red and green lights.
- If you can only see the white light and nothing else, you would look directly at the other boat’s stern as it drives away.
- Red and white means the boat is driving away from you, crossing from right to left.
- On the other hand, green and white signal that the vessel is moving away from you, crossing from left to right.
When renting a boat on Boatsetter , make it a habit of checking that navigation lights are working. You should turn on the navigation lights even if the sun is out. It’s the best and safest boating practice.
Want additional resources for boating?
Check out the links below for more information on boating.
- Navigation lights study guide
- Pre-departure boating checklist
- Boat Spring Commissioning Dewinterization Checklist
Don’t let your boat sit idly by. List it with us to earn $20K on avg.

Chuck Warren fell in love with boats at 9 years old while helping to restore his grandfather’s 1939 44-foot Elco cruiser. A lifelong boater, Chuck has experience operating large and small vessels on the waters of the Atlantic, Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean, and the Great Lakes.
During his 35-year marine industry career, Chuck has been the driver for several offshore powerboat racing teams, the chief engineer aboard a Caribbean research and salvage vessel, captain of a Florida Keys sunset cruise, and more.
Today, Chuck is a boating industry writer, copywriter, and captain who lives on his 40-foot boat in the summer when he isn’t delivering vessels around the Great Lakes or teaching new boaters to drive. Winters are split between the West Michigan lakeshore and wherever his travels take him.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

5 Best Lakes in Tennessee for Boating

Boatsetter Launches New, Limited-Time Summer Collection, Marking Another Milestone in Company's Experience-First Mission

How to Get a Boating License or Boater Safety Certificate

How to Create a Great Day on the Water for Your Renters
Sign up now for our WhatsApp newsletter and receive a FREE set of SVB playing cards!
Get the latest SVB news via WhatsApp!
- Product Selection Tool
- SVB@Youtube
- 0 My SVB Account
- Compare list
Are you missing items that you have already placed in your shopping cart? Log in to see your saved items.
- Boat Safety Equipment
Navigation Lights on Sailing Yachts and Motor Boats

Navigation lights ensure the safety of everyone at sea. The Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (IMO COLREG 72) precisely sets out the guidelines for navigation lights, i.e., displaying lights, their range (distance from which the light is visible), as well as how they should be constructed and assembled. Our guide is of interest to sailors and sports boats enthusiasts with boats up to 20 m in length.
Regulations and official certifications:
When must navigation lights be displayed, what are the regulations concerning the use of navigation lights at sea, how do i know that my lights are eu-compliant, what is a ce mark, how are navigation lights defined, minimum range of navigation lights:.
- From what distance must lights be visible?
- What lights are required for my boat?
What lights must be displayed on a sailboat or rowing boat with a motor?
What lights should i exhibit when at anchor, what lights should be displayed to show that a vessel is unable to manoeuvre.
- How do I indicate that my vessel has run aground?
Navigation lights – Conventional and LED:
What distinguishes led from conventional navigation lights.
- Replacement bulbs for conventional & LED lights
What are the advantages of LED navigation lights?
Switching from conventional to led navigation lights.
According to COLREGs part C, rule 20), navigation lights must always be used on board from sunset to sunrise or during the day if visibility is poor.
Please refer to the German Traffic Regulations for Navigable Maritime Waterways , §8 -10 and Preventing Collisions at Sea. Part C - Lights and Shapes. rules 20 - 31, and annexes I 1. - 14 for the exact wording.
NOTE: Vessels that are authorised to fly the German flag are generally only permitted to use approved navigation lights and sound signalling devices.
EU approval can be identified via the wheel mark symbol and the notified body number. BSH approved navigation lights (previously DHI) are marked with a model number (e.g., BSH/00/01/90).
However, even older lights with DHI approval that have already been installed maintain their approval, despite the changes made by the BSH.
In addition to the wheel mark symbol and German BSH approval, some lights are also approved by other countries, such as RINA (Registro Italiano Navale), MCA (Maritime and Coastguard Agency) and the USCG (United States Coast Guard). These are now recognised, provided the approval comes from the national approval body recognised in the country of origin.
National bodies whose accreditation is currently recognised in Germany:
| Canada: | Marine Safety Directorate |
| China: | CCS China Classification Society |
| Denmark: | Danish Maritime Authority |
| Finnland: | Finnish Maritime Administration |
| France: | Bureau Veritas S.A. |
| England: | Marine Safety Agency |
| Greece: | Ministry of Merchant Marine |
| Iceland: | Icelandic Maritime Administration |
| Italy: | Registro Italiano Navale |
| Japan | Nippon Kaiji Kyokai Material & Equipment |
| Croatia: | Croatian register of Shipping |
| Netherlands: | Directorate-General for Freight Transport, Shipping Inspectorate |
| Norway: | Sjofartsdirektoratet, Norwegian Maritime Directorate |
| Poland: | Polski Rejestr Statkow S.A. |
| Russia: | Russian Maritime Register of Shipping |
The wheel mark symbol indicates approval of the Marine Equipment Directive (MED). This approval is valid for all EU member states, both for commercial vessels and recreational shipping.
0098 = Notified Body number (here 0098 = Germanischer Lloyd in Hamburg) 18 = year in which the mark is affixed, here 2018

- A CE mark is a symbol that must be affixed to a product by the manufacturer before it is sold on the European market. It indicates that the manufacturer is aware of the specific requirements for the product in question and that it fulfils the requirements of relevant European product directives. A CE mark does not supersede approval according to collision prevention regulations.
- Navigation lights are defined in detail by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), according to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, 1972 (COLREGs) Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, 1972), in sections C and D. The following rules apply:
Which navigation lights are required on board according to IMO COL REG?
Definitions according to the 1972 International Regulations for Prevention of Collisions at Sea (COL REG 72):

1. Side lights for starboard and port
A green light on the starboard side and a red light on the port side, which shine from dead ahead in an arc of 112.5° aft to a point 22.5° abaft the beam (behind the beam) on either side of the vessel. On ships of less than 20 metres in length, the two individual sidelights may be replaced by a dual-colour combined light. This must be centrally located on the bow and stern axis.

2. Stern light
A white light mounted as close to the stern as possible and shines dead ahead in an arc of 135° (67.5° to each side). The mounting height should be aligned to the height of the side lights and should never be higher.

3. Three-colour light for sailing vessels (sailing lights)
On sail boats up to a length of 20 m, the side light and stern light can be combined into one three-colour light mounted on top of the mast. However, as soon as the sail boat's motor is engaged, the use of a three-colour light is no longer permitted. The rules for motor-powered vessels then apply.

4. Mast-head light
A white light placed over the centre line of the vessel and shines dead ahead in an arc of 225° (from straight ahead up to 22.5° more aft than crosswise to each side). The mounting height should be at least 1 m higher than the side lights. In the past, the mast-head light was also referred to as a steam boat light or steamer light, as it is only seen on ships that operate under engine power.

5. Signal light or all-round light
A light that shines in a complete circle of 360°. It may emit white, red or green light, depending on use. Examples of use: All sailboats and motorboats at anchor must exhibit a white anchor light . Ships over 12m in length must, if necessary, display vessel-in-distress lights (two red signal lights) placed at a vertical distance of at least 12 m. The distance between such lights must not exceed 1 m.
From what distance must navigation lights be visible?
The range indicates the distance from which the light can be seen. The minimum ranges of navigation lights are defined according to ship size as follows::
| Ships up to 12m in overall length | Range in nautical miles (NM) |
|---|---|
| Mast-head light | 2 NM |
| Side light (starboard /port) | 1 NM |
| Stern light | 2 NM |
| Three-colour light (sail boat when at sail) | 2 NM |
| All-round light (white, red, green all-round light) | 2 NM |
| Ships of 12 - 49 m overall length | Range in nautical miles (NM) |
|---|---|
| Mast-head light | 3 NM (up to 20 m) / 5 NM (from 20m) |
| Side light (starboard /port) | 2 NM |
| Stern light | 2 NM |
| Three-colour light (sail boat when at sail) | 2 NM |
| All-round light (white, red, green all-round light) | 2 NM |
| Ships from 50 m overall length | Range in nautical miles (NM) |
|---|---|
| Mast-head light | 6 NM |
| Side light (starboard /port) | 3 NM |
| Stern light | 3 NM |
| All-round light (white, red, green all-round light) | 3 NM |
Best-seller Hella Marine

Note: When sailing boats are powered by a motor, the rules for motorboats apply and not for sailboats. The tricolour light may then no longer be displayed.

Displaying lights for sailboats up to 20 m
1 x red port side light
1 x green starboard light
1 x stern light
Also allowed:
1 x red all-round light on or near the mast top
1 x green all-round light on or near the mast top

1 x 3-colour light

Sailing vessels under 7 m (dinghies or small sports boats)
If, due to their design, no modern lights can be fitted, sailing vessels under 7 m in length and vessels being rowed must always carry an electric torch or lantern showing a white light, ready to exhibit in sufficient time to prevent a collision.
1 x Electric light or a torch with white light

Motorised vessels over 12 m
Lights used must be either / or:
1 x white masthead light fore

1 x dual colour light

Motorised vessels under 12 m
Alternatively, motorised vessels under 12 m can exhibit the following lights:
1 x white all-round light

Motorised vessels under 7 m and 7 knots maximum speed (small motor boats, dinghies or inflatables):
Motorised vehicles under 7 metres and with a maximum speed of no more than 7 knots can display the following navigation lights: all-round lights, portside and starboard lights.
The following applies in accordance with German Traffic Regulations for Navigable Maritime Waterways (SeeSchStrO): If, due to their design, no lights can be displayed (e.g., dinghies), sailing vessels under 7 m in length and 7 knots maximum speed must carry an electric hand-held spotlight or a torch to prevent collisions in the dark.
Left: 1 x white all-round light, 1 x red port side light, 1 x green starboard light
Right: 1 x hand-held spotlight or torch
Best-seller Aqua Signal Conventional

Best-seller Aqua Signal LED

Provided no engine power is used, the rules for sailboats apply. Motor-sailing vessels must display a large black cone pointing downwards when sailing during the day or at good light.
For vessels travelling under sail or at rudder during darkness or at reduced visibility, the rules for carrying lights for motorised boats automatically apply. This then depends on the length of the boat.
By day with a black cone, tip pointing downwards.
Visual signalling equipment

Torches % Spotlights

How must navigation lights be mounted on board?
Navigation lights must be securely mounted perpendicular to the waterline. Mast-head lights and stern lights should both be placed above the keel line.
At anchor during daylight? This must be displayed with a black anchor ball.
If the vessel is anchored outside of an area of water known by the River and Shipping Police Authority as an anchorage and berth for small vessels, this must be indicated as follows:
A black ball by day, 1 x white all-round light at night

Anchor Lights

If your boat is unable to manoeuvre*, this should be indicated as follows:
Stationary: 2 x red all-round light, 2 x black ball, one below the other (during the day)
Moving: 1 x red port side light, 1 x green starboard light, 1 x white stern light
* A vessel is described as if, due to exceptional circumstances (e.g., rudder failure or engine malfunction), it cannot manoeuvre as prescribed and therefore cannot avoid another vessel.

How do I indicate correctly that my sailboat or motorboat has run aground?
If your boat has run aground, this should be indicated as follows:
2 x red all-round light, 1 x white all-round light, 3 x black ball, one below the other (during the day)
Manufacturers that specialise in navigation lights such as Aqua Signal or Hella Marine supply a wide range of internationally approved navigation lights which work with conventional (with BSH bulb) or with permanently installed light-emitting semiconductor components (LEDs). The bulbs required for operation are an integral part of the approval. Replacement bulbs must also be certified so that approval / your insurance protection is guaranteed. Ships under 20 m: Stern and anchor lights require BSH-approved light bulbs with 10 watts, all other navigation lights 25 watts.
| Spare light bulb for series | Stern l / Anchor l. 12 V/10W | Stb./BB, Masth / All-rnd l. 12 V / 25W |
|---|---|---|
| Aqua Signal, Serie 40 | SVB Art. Nr. 10203 | SVB Art. Nr. 10206 |
| Aqua Signal, Serie 41 | SVB Art. Nr. 10203 | SVB Art. Nr. 10206 |
| Aqua Signal, Serie 50 | SVB Art. Nr. 10203 | SVB Art. Nr. 10206 |
| Hella Marine, Serie 2984 | SVB Art. Nr. 10203 | SVB Art. Nr. 10206 |
All series listed above with BAY15d sockets could alternatively be operated with a high-Power LED . The big advantage in doing so is that the LED is suitable for multiple voltages (10-30 V) and consumes just 3 watts during operation. Since the light colour, range of light or beam angle can vary depending on the housing, this light is NOT yet internationally approved.
Spare Bulbs - Conventional & LED

Energy consumption on sailing ships is, as ever, a topic of significant interest. This is especially true for blue-water sailors who like to sail longer distances at a stretch. The arguments for converting to LED technology are as follows:
- High energy savings due to the low power consumption
- Long lifespan (over 10,000 hours)
- MultivoltTM technology (10-30V) with greater tolerance to voltage peaks
- Compact and light housing constructions
- Waterproofed, hermetically sealed housings
- Maintenance free
When switching completely from conventional navigation lights to LED lights, lights with the BSH seal of approval / EU wheel mark meet all the requirements in terms of light colour (no risk of blue tint), range of light and beam angle, and that you are travelling in accordance with KVR.
Navigation lights with LED technology

Replacing your navigation lights is often easy to do as manufacturers usually use the same mounting points for LED lights or have an adapter plate for further use of existing drill holes:

| Existing series: | New LED series: |
|---|---|
| Aqua Signal, Series 40 with quicfit socket | Series 34 with quicfit socket |
| Aqua Signal, series 41 | Series 41 (use identical drill holes) |
| Aqua Signal, series 40 and 50 | Series 43 using adapter plate, SVB no. 14557 |
| Aqua Signal, series 40 and 50 | Series 44 using adapter plate, SVB no. 14557 |
Share our guide on social media

Written by our SVB (technical) experts
Our SVB safety experts regularly carry out maintenance checks and tests on our safety products, such as life jackets, life rafts etc. They test products and base their recommendations on many years of experience and their own know-how.
Candlelight vigil held for Old Saybrook boating accident victims
By jeremy chen • published september 8, 2024 • updated on september 8, 2024 at 9:56 am.
Paying respects to the lives lost in Old Saybrook. The community, family, and friends held a candlelight vigil Saturday night for the three men who died after a boat crash Monday.
Candles being held closely light up the Saybrook Point Marina Saturday night. The Old Saybrook community coming out to remember the three men that died in a boating accident Monday: Christopher Hallahan, Ian Duchemin, and Ryan Britagna . Flowers being thrown from a boat into the water to pay respects to them.
Free 24/7 Connecticut news stream: Watch NBC CT wherever you are
“There was just so many people here so really it was just a nice outpouring by the community to just show up. It was very nice,” Dennis Hallahan, the uncle of Christopher Hallahan said.
He says the family has been in mourning over his passing, but the community support has helped with them coping.
Get top local stories in Connecticut delivered to you every morning. Sign up for NBC Connecticut's News Headlines newsletter.
“We’re struggling, but we’re getting by from these types of acts and all being together and the community coming together has been very, very nice,” Hallahan said.
The lights from the candles being held, also was a message about putting lights on the jetty where the boat crash happened. The idea is to help prevent future crashes at the mouth of the Connecticut River.
“It would be a simple thing to do. It can only help. It can only save lives,” he said.

Bridgeport teachers raise concerns about start of school year

Gen Z voters keep close tabs on upcoming presidential election
Hallahan says while this has been a difficult week, the support they’re getting is appreciated.
“It really helps the family cope with this. We’ve been with the family all week. It’s really been a tremendous outpouring,” he said.
This article tagged under:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For most small vessels, motoring requires red and green (port and starboard) lights, and a white light visible in all directions around the boat. This is almost always a stern light and a masthead light on sailboats. Boats under sail require port and starboard lights, and a white stern light. Sailboats below sixty-five feet may show a tricolor ...
Sailboats must have the same red and green lights as powerboats. The difference is that you'll need other ones on the stern and mast. If your boat is less than 65 feet, you can use either a combination of a bicolor light with red and green along with another at the stern or a tricolor one on top of the mast.
A properly lit sailboat at night is a boat that is equipped with the correct navigation lights, which are required by law. These lights must be visible for two miles and should include a green light on the starboard side, a red light on the port side, and a white light aft. Additionally, the boat must also have a white masthead light that is ...
==Short answer sailboat navigation lights:== Sailboat navigation lights are essential safety features that help vessels communicate and avoid collisions at night. These lights, such as the red and green sidelights and white stern light, allow sailors to determine the direction and status of approaching boats. Understanding the Importance of Sailboat Navigation LightsUnderstanding the Importance of
Boats less than 12 meters or 39.4 feet long: You'll need one red light and one green light at the front port and starboard sides of the boat for these boats. These lights should be positioned so that they can be seen at an angle of 112.5 degrees. The sidelights should be strong enough to be seen from a mile away.
The basic rule is that sidelights and a stern light are required. Permissible variations to this rule appear below. Sailboats less than 20m (65.7') can substitute a tricolor light for separate sidelights and stern light—or a bi-color light and a stern light may be substituted. Sailboats less than 7m (23') shall, if practicable, exhibit lights ...
Power driven boats on the Great Lakes may carry an all around white light in stead of a second masthead light and stern light combination. Sidelights - Colored lights - red on port and green on starboard - showing an unbroken arc of the horizon of 112.5 degrees, from dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on each side.
Powerboat under 23 feet (7m) Powerboats under 23 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed: One white masthead light visible for 2 miles. One red & green sidelight visible for 1 mile. One stern light visible for 2 miles. One white, red, green, or yellow all-round light visible for 2 miles.
The most common of our navigation lights are our "running lights". This is a red light on the port side of the boat and a green light on the starboard side that shine from the bow to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam of the boat. This creates a 112.5-degree arc on either side of the vessel. To complete a 360-degree circle, our white stern light ...
The rear of the boat should have a white stern light visible at 135 degrees and two miles away. You will also need green and red sidelights visible from at least a mile away and at 112.5 degrees. There is an exception for sailboats of seven meters or longer. A tricolor light can be used only if the boat is powered by sails and not a motor.
Human-powered boats are required to display a white light that can be seen from all sides. Otherwise, they are permitted to follow the light requirements for sailboats, according to vessel length. Navigation light requirements for sailboats Sailboats under 7 m. Sailboats under 7 m must display green and red sidelights and a stern light.
Sailboats are required to have three lights at a minimum: a masthead light, a red port light, and a green starboard light. The masthead light is white and is located at the top of the mast. This light should shine forward and aft and be visible from 2 nautical miles away. It is important to ensure that the masthead light is not obstructed by ...
Powered boats under 39.4 feet: One all-around white light, visible from all directions (360 degrees) from two nautical miles away. This light must be attached at least 39 inches above the sidelights. One green starboard and one red port sidelight, visible across 112.5 degrees from one nautical mile away.
As such a power boat, and by extension all sailboats, MUST, without question show one green light on the starboard bow and one red light on the port bow and one all around white light or lights while operating in reduced visibility. These lights should shine at all 360 degrees of visibility with the bow lights shining at an angle of dead ahead ...
The starboard side light is green. When looking at the boat's transom or stern, a white light may be visible. Keep in mind large boats and ships may use other colors, like yellow. Next time you're boating at night, say thanks to your navigation lights. They allow you to see other boaters in the dark and help prevent collisions.
Nice Dream Sailboat Night Light for Kids, 3D Ship Illusion Lamp, 16 Colors Changing with Remote Control, Room Decor, Gifts for Children Boys Girls. 4.6 out of 5 stars 480. $7.99 $ 7. 99. FREE delivery Mon, Nov 27 on $35 of items shipped by Amazon. Or fastest delivery Fri, Nov 24 .
Sailboat Night light suncatcher made of fused stained glass RED Sail White and blue water scene FREE Shipping (44) $ 34.27. FREE shipping Add to Favorites Mixed Metals Sailboat Sculpture Night Light, Night Lamp, Capiz Shells on Sail, Handmade, Hand-painted, Gold, 17.5" Tall, Phillipines, 1980s (419) $ 78.00. FREE shipping ...
Ocean Sailboat Night Lamp, Epoxy Resin Wood Night lamp, Model Ocean Miniature Ocean, Resin Lamp For Bedroom, Night Light, Gift for him. (21) $164.50. $329.00 (50% off) FREE shipping. Sailboat Night Light made with Genuine Stained Glass. Great for Kid's Room, Bathroom, or other Dark Room.
Boat Navigation at Night: Head-on Approach. If you meet a vessel and see a green, red and white light, you are approaching another power-driven vessel head-on. ... flashlight or lighted lantern showing a white light (this rule applies if the boat cannot be equipped with standard navigation lights). 3) You are approaching an anchored craft at night.
2. Stern light. A white light mounted as close to the stern as possible and shines dead ahead in an arc of 135° (67.5° to each side). The mounting height should be aligned to the height of the side lights and should never be higher. 3. Three-colour light for sailing vessels (sailing lights) On sail boats up to a length of 20 m, the side light ...
Colorful Hand Painted Sailboat Night Light, Stained Glass Nightlight, Lake House Light, Beach House Nightlight, Sailing Decor, NLSB10-11 (3.1k) $ 28.95. Add to Favorites Sailboat with Orange Sun Stained Glass Nightlight (1.1k) Sale Price $42.00 $ 42.00 $ ...
At anchor, vessels need an all-round white anchor light. What About at Night? Between sunset and sunrise, boats must display navigation lights (those are the red and green lights on the bow of your boat). Masthead and stern lights are also crucial for night time navigation. These bright white lights make your boat visible to other boaters in ...
Portable Marine LED Boating Lights, LED Night Light for Boat Bow or Stern, Battery Operated Dinghy Navigation Lights, Backup Illumination for Kayak Racing Sailboats and Inflatable Boats . Brand: Deals4you. 4.1 4.1 out of 5 stars 256 ratings | Search this page . Currently unavailable.
Boat Navigation Lights, Navigation Lights for Boats Led, Boat Lights for Night Fishing, Boat Red and Green Bow Lights, Deck Lights for Marine, Yacht, Kayak, Bass Boat, Pontoon Boat. 44. 200+ bought in past month. $1199. Save 5% on 3 select item (s) FREE delivery Tue, Mar 19 on $35 of items shipped by Amazon. Or fastest delivery Mon, Mar 18.
Paying respects to the lives lost in Old Saybrook. The community, family, and friends held a candlelight vigil Saturday night for the three men who died after a boat crash Monday. Candles being ...